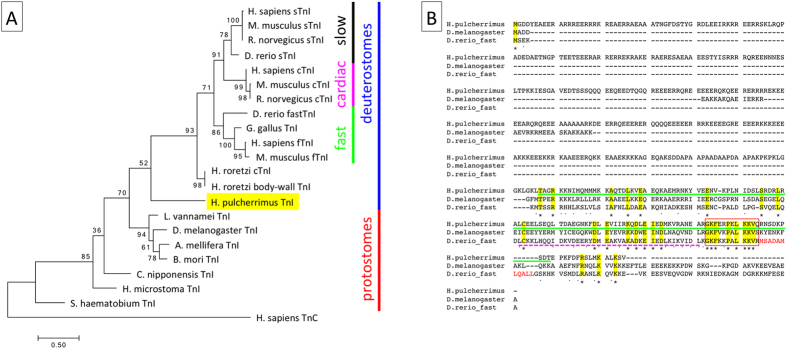
Figure 1. Sea urchin has a TnI gene.
(A) The phylogenic tree of TnI based on the C-terminal troponin motif indicates that the sea urchin TnI forms a sister group with chordate TnI. The number at each branch point is the bootstrap value (n = 500). In vertebrates, TnI is categorized into three groups: slow, cardiac, and fast TnIs. H. sapiens troponin-C (TnC) was used as the outgroup. Accession numbers for each TnI are listed in the Table 1. The bar indicates evolutionary distance. (B) The alignment of TnI from sea urchin, fly and zebrafish. The red square indicates the inhibitory region. The magenta and green underlines indicate the positions of the TnT binding site and of the amino acid sequence equivalent to the position of the antigen of Mesocentrotus nudus TnI, respectively. The red characters in the zebrafish sequence indicate the switch region.