Fig. 2.
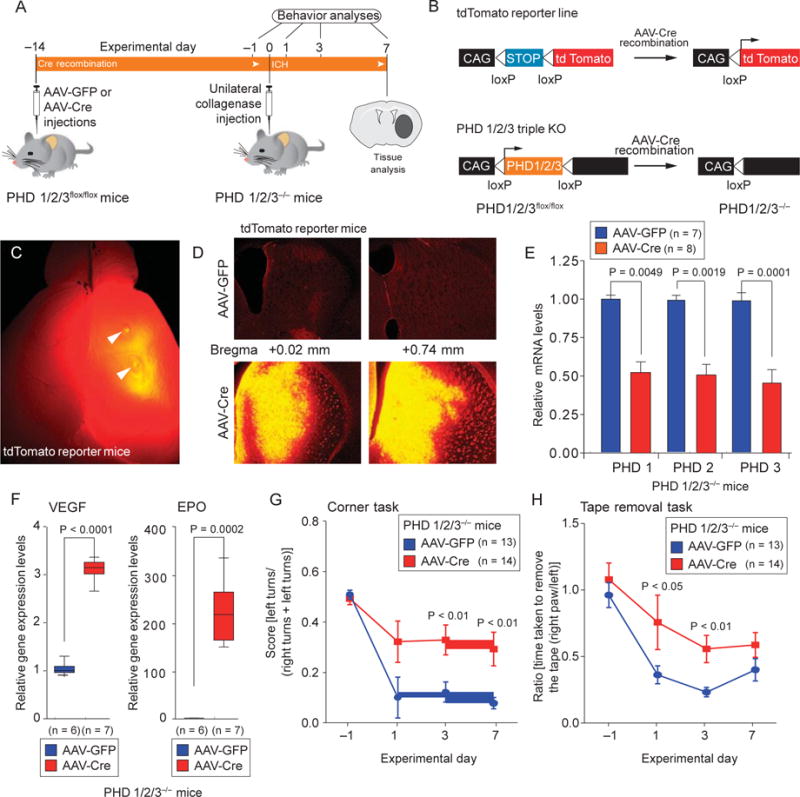
Molecular reduction of HIF-PHD isoforms in the mouse striatum enhances functional recovery after ICH. (A and B) Scheme for validating AAV8-Cre activity and selective deletion of PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3. KO, knockout. (C) Effective recombination by injection of AAV8-Cre into the mouse striatum was verified using a tdTomato floxed reporter. (D) Coronal sections of the tdTomato mouse brain revealed that tdTomato reporter expression was highest mediolaterally at coordinates corresponding to subsequent hemorrhagic stroke. Scale bars, 1 mm (C); 100 mm (D) (E) Quantitative PCR confirmed reduction of PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 expression in the striatum of AAV8-Cre– injected mice but not in the striatum of AAV8-GFP–injected mice (E). (F) Quantitative PCR confirmed that reduction of striatal PHD expression led to increases in the HIF- dependent genes encoding VEGF and EPO in the mouse striatum. (G and H) Conditional reduction of HIF-PHDs enhances functional recovery in mice after ICH, as shown by two behavioral tasks: the corner task (G) and the tape removal task (H). Significance was determined by two-tailed t test (E and F) or two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (G and H). All graphs show the means ± SEM
