Figure 6.
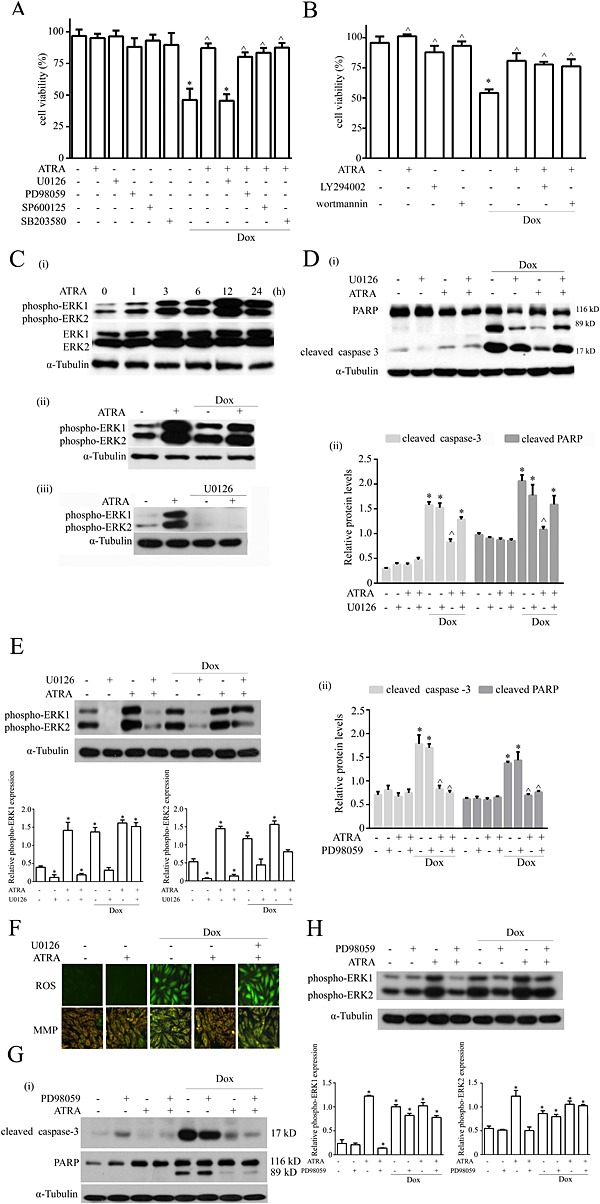
U0126 attenuates the cardioprotective effect of ATRA against doxorubicin‐induced damage in H9c2 cells. Effects of (A) MAPK and (B) Akt signalling pathway inhibitors on the protective effect of ATRA against doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity (n = 5) (C) Western blotting for the effect of ATRA and U0126 on phosphorylated ERK1 and ERK2. (i) Doxorubicin and ATRA induced ERK1/2 activation in a time‐dependent manner. (ii) Effect of ATRA on ERK1/2 activation in doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity. (iii) U0126 inhibited ATRA‐induced ERK1/2 activation. Western blotting for the inhibitory effects of (D) U0126 and (G) PD98059 on the protective effect of ATRA on doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells, and quantitative analysis of apoptosis‐associated proteins (cleaved caspase‐3 and cleaved PARP). Quantitative values are computed as the ratios of the density of the targeted protein to that of α‐tubulin (n = 5). Western blotting for the effects of (E) U0126 and (H) PD98059 on phosphorylated ERK1 and ERK2 through inhibition of the ATRA effect on doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity and semi‐quantitative analysis of ERK1 and ERK2. Quantitative values are computed as the ratios of the density of the targeted protein to that of α‐tubulin (n = 5). (F) ROS generation (DCFH‐DA staining) and the MMP (JC‐1 staining) abolished the protective effect of ATRA on doxorubicin‐induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells. Representative images from each group (n = 6) are presented. Except as noted, the concentrations of ATRA and Dox were 2 and 3 μmol·L−1, respectively, the concentrations of inhibitors U0126, SB203580, SP600125, PD98059 and LY294002 were each 50 μmol·L−1, and the concentration of wortmannin was 1 μmol·L−1. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM and were analysed by anova. *P < 0.05 versus control and ^P < 0.05 versus Dox.
