Figure 2.
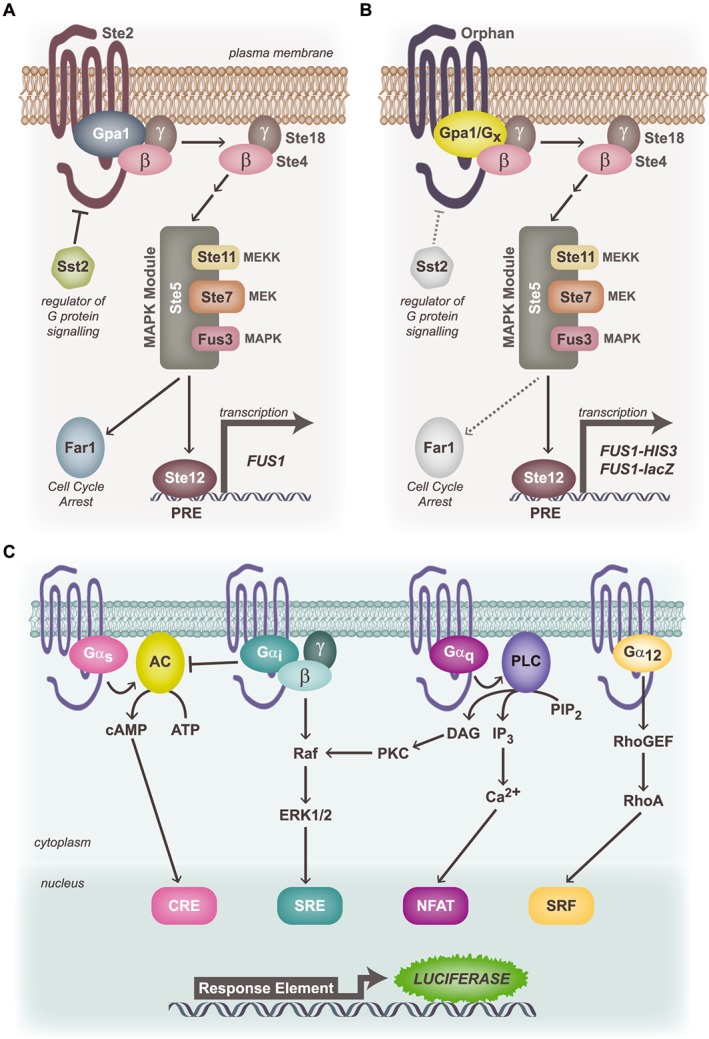
Assays for the identification of G protein signalling pathways using the constitutive activity of an orphan GPCR. (A) Yeast GPCR signalling pathway. The yeast pheromone receptor, Ste2, couples to the endogenous yeast heterotrimeric G proteins (Gα = Gpa1) to drive Gβγ‐mediated (MAPK) pathway activation and Ste12‐mediated transcription via the pheromone‐response element (PRE). MEK: MAPK kinase; MEKK: MEK kinase. (B) Modified yeast G protein signalling assay: chimeric versions of Gpa1 bearing the final five amino acids of each of the human Gα proteins have been introduced into yeast strains lacking each of the yeast GPCR, Ste2, the regulator of G protein signalling, Sst2, and the cell cycle arrest protein, Far1. Upon transformation with the orphan GPCR of interest, constitutive coupling to a specific G protein chimera drives the MAPK module to stimulate transcription of HIS3 (facilitates selection and expansion in HIS3‐deficient media) and the lacZ reporter via FUS1. (C) Mammalian reporter assays for transcription factors downstream of each of the major G protein families. Constitutive coupling via Gαs leads to stimulation of AC and generation of cAMP, which stimulates transcription of luciferase that lies downstream of a cAMP response element (CRE). Likewise, Gαi activity is reported via the serum response element (SRE) upon Gβγ signalling to ERK1/2 MAPK; Gαq via nuclear factor of activated T‐cells (NFAT) and Gα12 via serum response factor (SRF) response element.
