Figure 1.
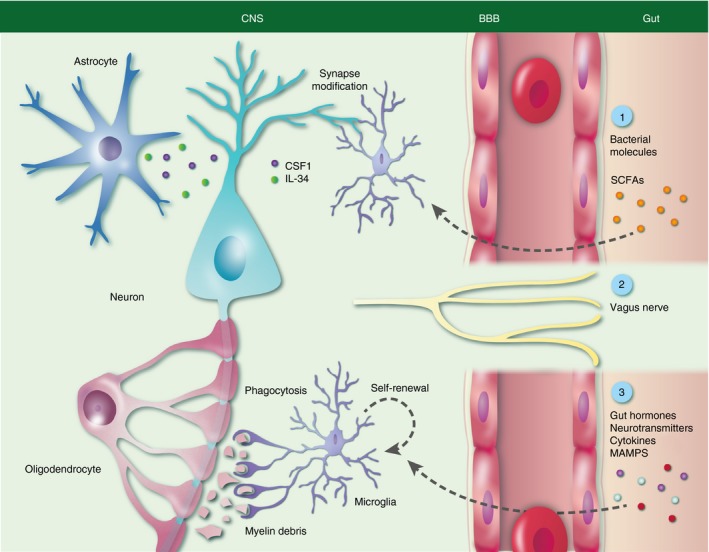
Microglia functions under homeostatic conditions and its modulation by host microbiota. During adulthood cortical microglia survey mature neurons and are involved in learning‐induced dendritic spine formation and nourish neurons. Furthermore, colony‐stimulating factor 1 (CSF‐1), interleukin‐34 (IL‐34) and short‐chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are important components for microglia function and maturation. Direct signalling via the vagus nerve and other molecules like gut hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines or microbial‐associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) may also affect microglia.
