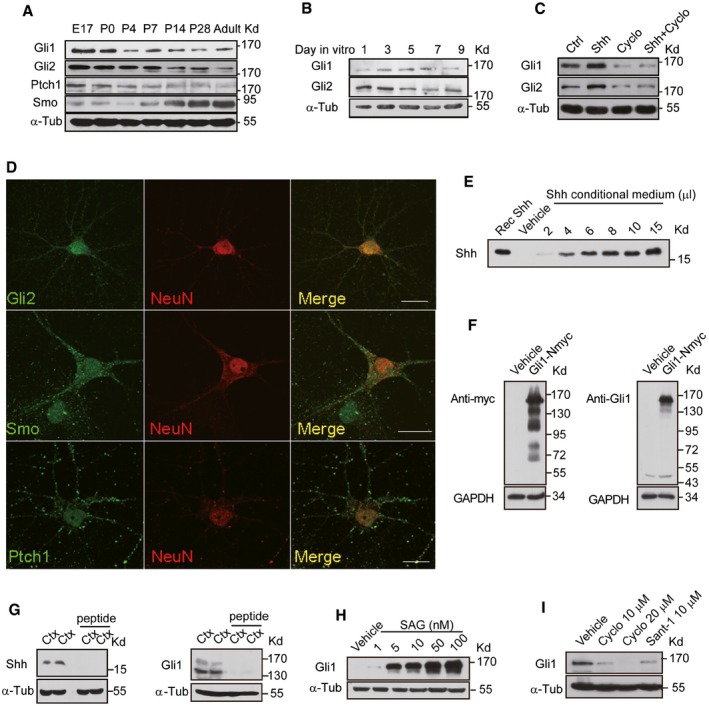
-
A–C
Western blots of the total lysates extracted from rat hippocampus at different developmental stages (A), from cultured hippocampal neurons at different days in vitro (B) and neurons treated with either vehicle (Ctrl), Shh, cyclopamine (Cyclo), or Shh plus Cyclo for 24 h (C) with the indicated antibodies.
-
D
Representative immunostaining of cultured hippocampal neurons with the indicated antibodies. Scale bar: 10 μm.
-
E
Western blots of the medium from HEK293 cells transfected with empty vectors (Vehicle) or Shh construct by the anti‐Shh antibody. The numbers indicate different loading volume (μl) of conditional medium. Recombinant Shh (Rec Shh; Sigma) was used as a positive control.
-
F
Total lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with empty vectors (Vehicle) or myc‐tagged Gli1 construct (Gli1‐Nmyc) were Western‐blotted and analyzed with the anti‐myc antibody (left) or the anti‐Gli1 antibody (right).
-
G
Western blots of cortical extracts from mice using Shh (left) or Gli1 (right) antibodies with or without pre‐incubation of antigenic peptide.
-
H, I
The expression level of Gli1 detected by Western blots of lysates from NIH3T3 cells incubated with SAG (Smoothened agonist) at the indicated concentrations (H) or from hippocampal neurons incubated with Cyclo or Sant‐1 at the indicated concentrations (I).
Data information: α‐Tubulin (α‐Tub) and GAPDH were used as loading controls.