Figure 1.
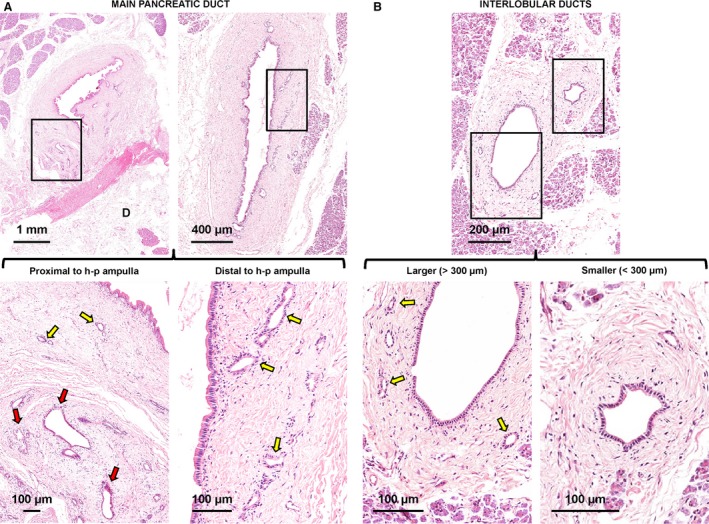
Distribution of pancreatic duct glands (PDGs) within pancreatic ducts. (A) Haematoxylin‐eosin stains of main pancreatic duct. The main pancreatic duct displays glandular elements called PDGs that are located within its wall. The PDG area is strictly correlated with the duct diameter. Near the hepato‐pancreatic ampulla, the main pancreatic duct displays two types of glands: intramural (yellow arrows) and extramural (red arrow) PDGs. Distal to the hepato‐pancreatic ampulla, only intramural PDGs could be recognized. The area in the boxes is magnified in the lower images. D, duodenum (wall: sub‐mucosal layer). (B) Haematoxylin‐eosin stain of pancreas. At the level of interlobular pancreatic ducts, PDGs (yellow arrows) are present only in larger ducts (diameter > 300 μm: left images). Smaller interlobular ducts (diameter < 300 μm: right images) do not contain PDGs. Areas in the boxes are magnified in the lower images.
