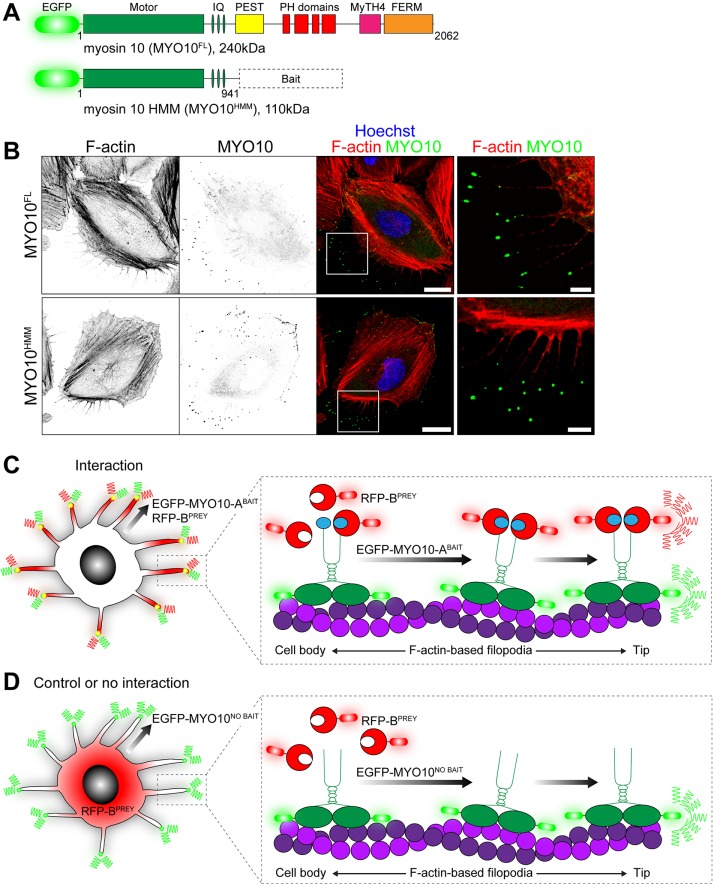
FIGURE 1:
Principle of the nanoscale pulldown (NanoSPD). (A) Domain representation of full-length EGFP-tagged MYO10FL with the ATPase motor domain, IQ motifs that bind light chains, a coiled-coil and tail domains that bind cargo. Heavy meromyosin MYO10HMM molecules are identical but truncated after the coiled-coil. Query bait proteins are fused to the C-terminus of MYO10HMM. (B) EGFP-tagged MYO10FL (top panel) and truncated MYO10HMM (bottom panel) traffic to filopodial tips in HeLa cells. Inset white boxes are shown magnified. F-actin is labeled with rhodamine phalloidin (red), and nuclei are stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: 20 µm; 5 µm (inset). F-actin and MYO10 images have been uniformly inverted. (C) Using NanoSPD to test the interaction between ABAIT and BPREY proteins. ABAIT is forcibly trafficked to filopodial tips by MYO10 as part of the EGFP-MYO10-ABAIT fusion protein (green). In the presence of an interaction, RFP-BPREY molecules (red) are actively cotransported along filopodia, resulting in concentration of bait and prey molecules at filopodial tips. (D) In the control, EGFP-MYO10NO BAIT molecules (green) lacking a bait still accumulate at filopodial tips but no longer traffic RFP-BPREY (red). Identical results are expected if RFP-BPREY does not interact with EGFP-MYO10-ABAIT.