Table 1.
DNA binding, in vitro and in vivo antitrypanosomal activity of the DAPI analogues.
| Compound | Code | ΔTma (°C) | Cytotoxb (μM) | T. b. rc (nM) | SId | In vivof(cures) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
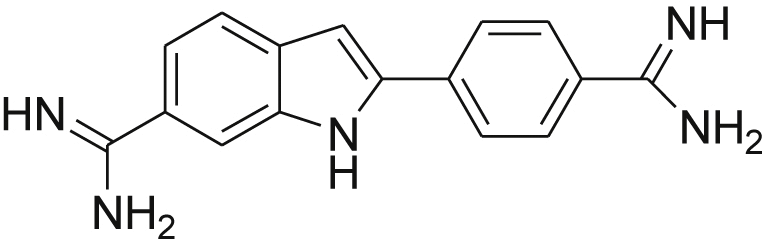 |
DAPI | >27 | 0.86 | 18 | 48 | 2/4 |
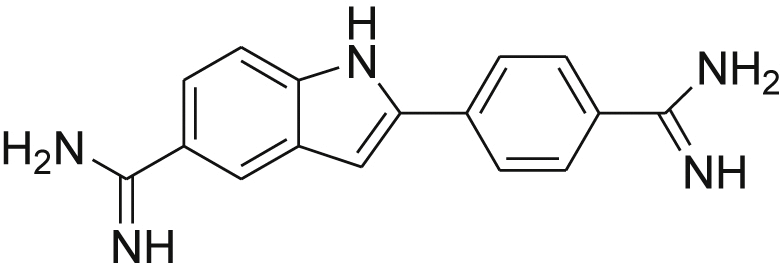 |
5a | 19.2 | 1.7 | 3 | 566 | 0/4 |
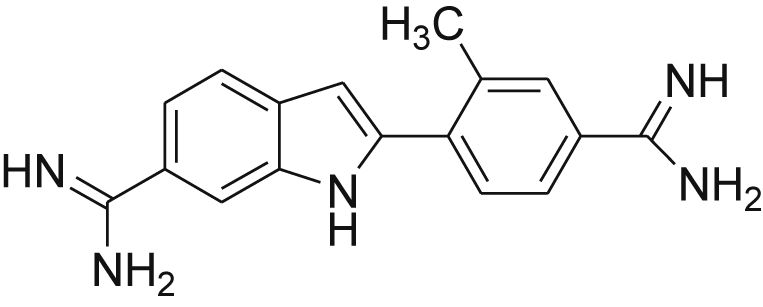 |
5b | >26 | 15.7 | 5 | 3140 | 3/4 |
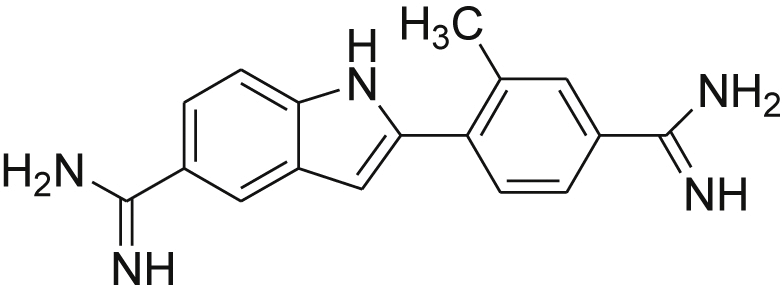 |
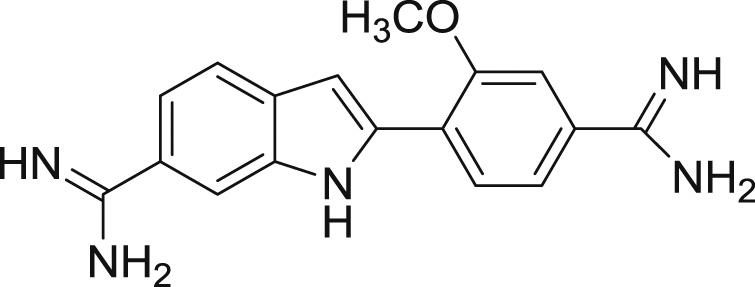
5c | 15.3 | 23.5 | 3 | 7833 | 3/4 |
 |
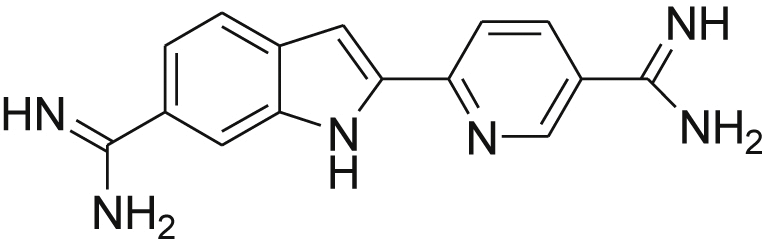
5d | >26 | 29.6 | 6 | 4876 | 4/4 |
 |
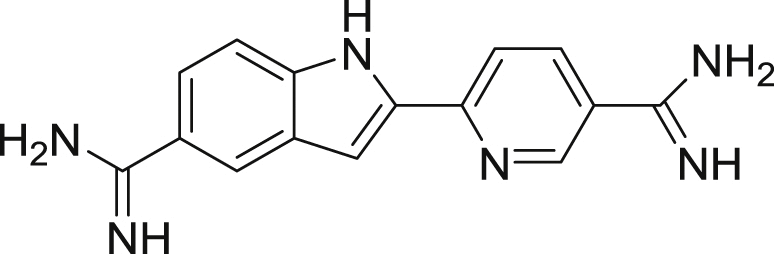
5e | 22.1 | 3.2 | 24 | 133 | 4/4 |
 |
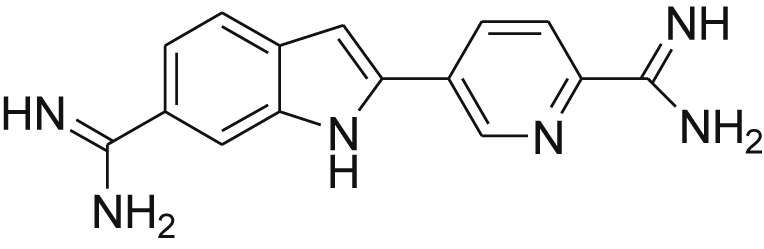
5f | >26 | 21.3 | 4 | 5325 | 4/4 |
 |
5g | 15.3 | 2.0 | 3 | 666.7 | 1/4 |
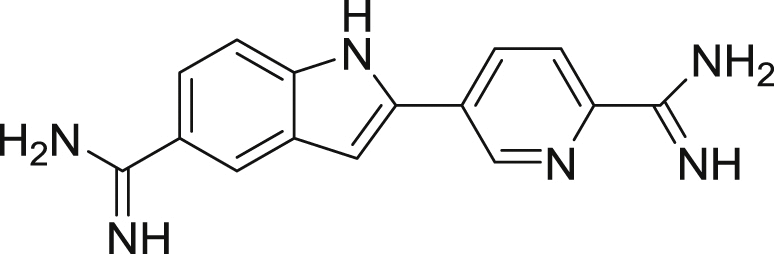 |
5h | 12.1 | 1.8 | 5 | 394 | 1/4 |
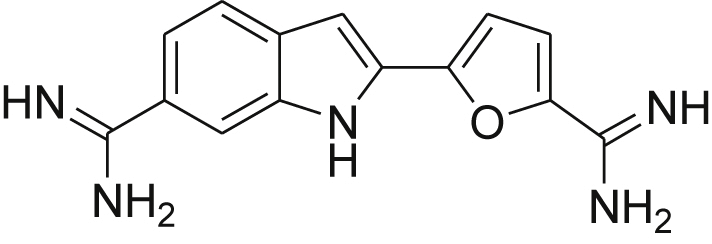 |
5i | 11 | 7.2 | 9 | 800 | 0/2 |
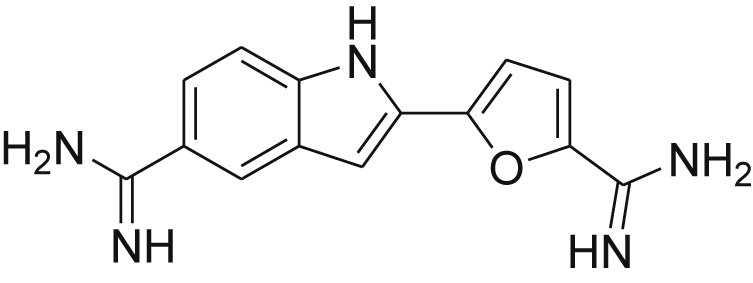 |
5j | 21.4 | 2.7 | 3 | 900 | 4/4 |
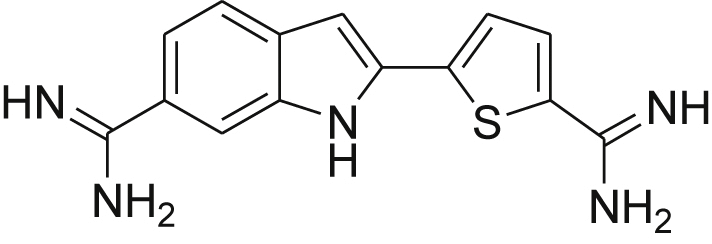 |
5k | 10 | 4.5 | 11 | 409 | 0/4 |
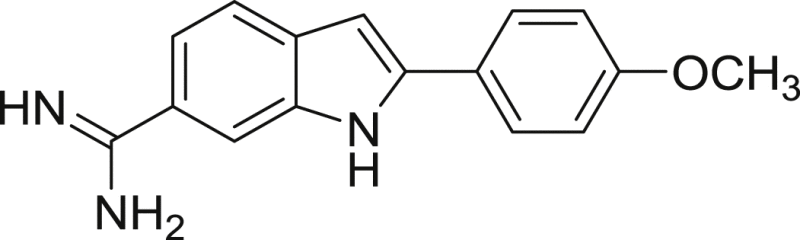 |
8 | 12.6 | 29 | 4869 | 6 | NDe |
Increase in thermal melting of poly (dA-dT)n.
Cytotoxicity was evaluated using cultured L6 rat myoblast cells.
The T. b. r. (Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense) strain was STIB900. The values are the average of duplicate determinations.
Selectivity Index for T. b. r. expressed as the ratio: IC50 (L6)/IC50 (T.b.r.).
Not determined as in vitro inactive.
In vivo efficacy was determined in T. b. rhodesiense (STIB900) infected mice at 4 × 5 mg/kg i.p. dose.
