Figure 5. APS attenuates doxorubicin-induced heart injury by regulation of the phosphorylation of AMPK/mTOR.
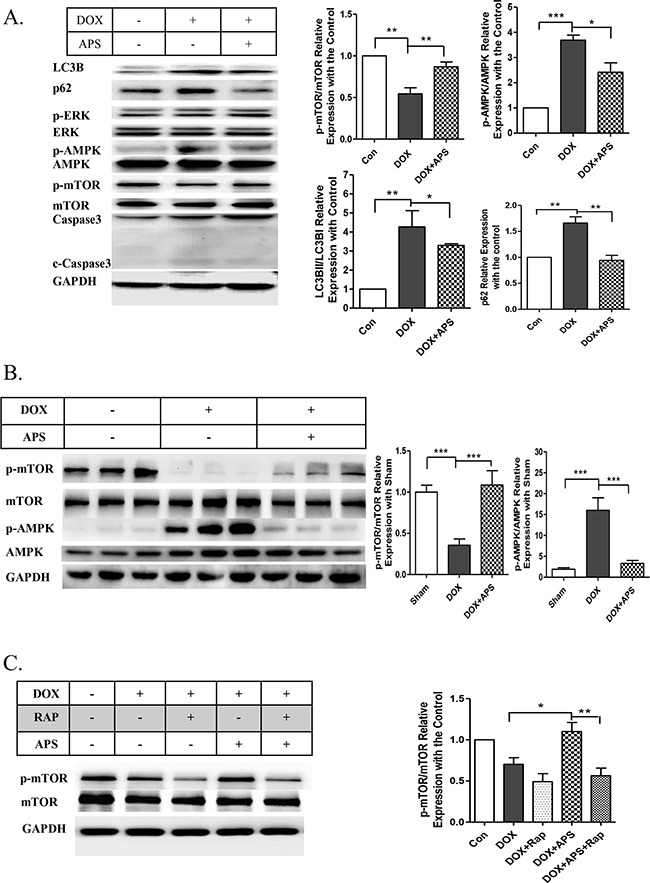
A. APS (50 μg/ml) attenuateddoxorubicin (0.5 μM)-induced increased AMPK phosphorylation and decreased mTOR phosphorylation, as assayed by Western blots (n = 5). B. Western blot and average data for AMPK/mTOR phosphorylation in the hearts of sham, DOX, and DOX+APS pretreatment groups (n = 8). C. The protective effect of APS was reversed by the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. The NRVMs were pretreated with 100 nM rapamycin for 1 h before APS (50 μg/ml) and DOX (0.5 μM) treatment. mTOR was analyzed by Western blots (n = 5). (*P<0.05, **P <0.01, ***P<0.001).
