Fig. 3.
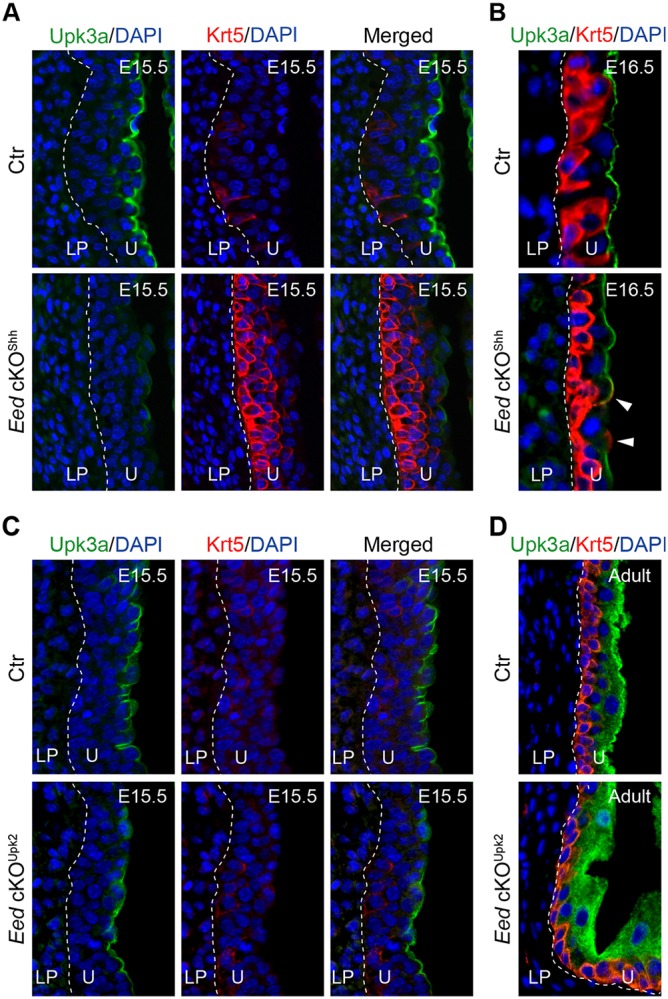
Deletion of Eed from embryonic urothelial progenitors leads to premature differentiation of Krt5+ basal cells and delayed formation of Upk3a+ superficial cells. Immunofluorescence microscopy of bladder sections stained for Upk3a (green), Krt5 (red) and DAPI (blue). (A,B) control (Ctr, Eedf/+;ShhGC/+) and Eed cKOShh bladder sections from E15.5 (A) and E16.5 (B) embryos. (C,D) Control (Ctr, Eedf/+;Upk2-Cre) and Eed cKOUpk2 (Eedf/f;Upk2-Cre) bladder sections from E15.5 (C) and adult (D) mice. White dashed lines demarcate the different layers within the bladder. Arrowheads indicate superficial cells that express both Upk3a and Krt5. U, urothelium; LP, lamina propria.
