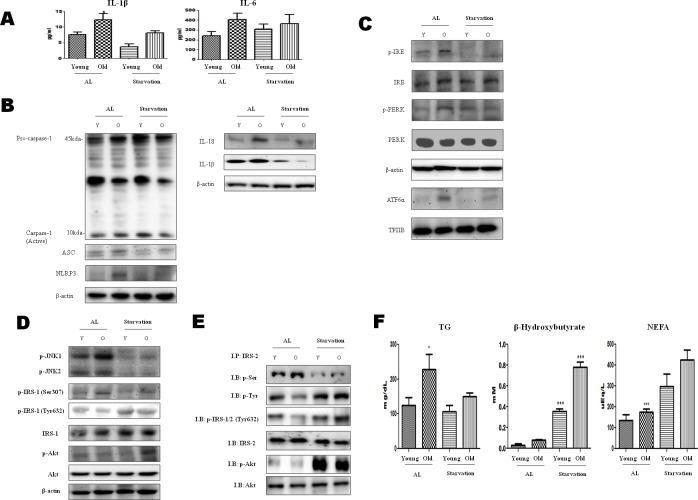
Figure 1. Modulation of ER-stress-induced inflammasome formation in acute starvation rat liver.
A. IL-1β and IL-6 levels were determined in the serum. Results of one-factor ANOVA: *p < 0.05 vs. Ad libitum. B. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the inflammasome levels in the cytoplasmic extracts. As shown, the protein levels of the inflammasome were decreased by acute starvation. C. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the protein levels of UPR markers. As shown, the levels were significantly decreased in the starvation model. One representative blot of each protein is shown from three experiments that yielded similar results. D. Western blot analysis was performed to detect the presence of insulin signaling in the cytoplasmic extracts. The protein levels of serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and phosphorylation of Akt were decreased by starvation. In contrast, tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 was increased. E. IRS-2 interaction of Akt and its modulation by starvation. cytosol extracts were prepared from young and old rat livers. Immunoprecipitated IRS-2 was determined to be physically associated with p-seine, p-tyrosine, p-IRS-1/2 (t632), p-Akt, and Akt by Western blotting. F. Constituents were determined in the serum. Results of one-factor ANOVA: *p < 0.05 vs. Ad libitum.