Figure 5. RIP1-ROS-JNK-c-Jun signaling pathway is involved in H2-18-induced programmed cell death.
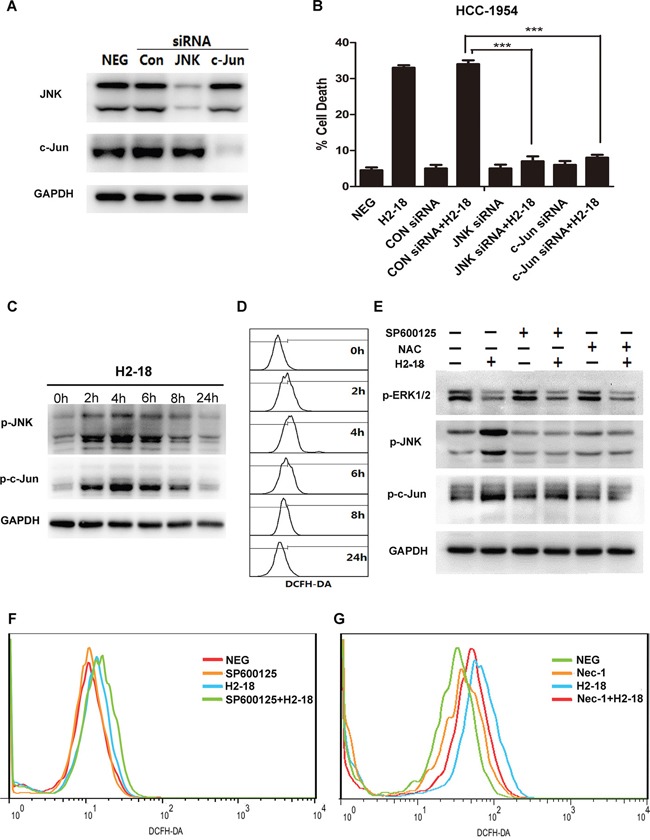
A. Immunoblots determining knockdown of JNK or c-Jun by siRNA in HCC-1954 cells. B. The effects of knockdown of JNK or c-Jun on H2-18-induced cell death in HCC-1954 cells. Data are shown as means ± SD. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ANOVA. C. Immunoblots examining the level of pJNK and p-c-Jun in HCC-1954 cells treated with 10 μg/ml H2-18 at indicated time. D. DCFH-DA was detected by flow cytometry to measure the level of ROS production at indicated time in H2-18-treated HCC-1954 cells. E. Immunoblots detecting the effects of JNK inhibitor SP600125 or ROS scavenger NAC on pERK1/2, pJNK and p-c-Jun in H2-18-treated HCC-1954 cells. F. DCFH-DA was detected by flow cytometry to measure the level of ROS production in HCC-1954 cells treated with control IgG, JNK inhibitor SP600125, H2-18, and SP600125 plus H2-18. G. DCFH-DA was detected by flow cytometry to measure the level of ROS production in HCC-1954 cells treated with control IgG, necrosis inhibitor Nec-1, H2-18, and Nec-1 plus H2-18. Every experiment was repeated 3 times.
