Figure 4. D16F7 inhibits migration and vasculogenic mimicry of murine melanoma cells.
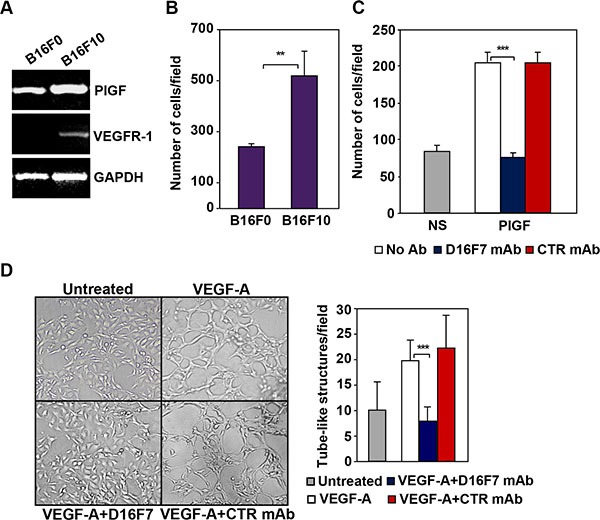
(A) B16F10 cells but not B16F0 cells express VEGFR-1. PlGF and VEGFR-1 expression in B16F0 and B16F10 cells was evaluated by RT-PCR analysis. (B) B16F10 cells are characterized by a highly invasive phenotype. The ability of B16F0 and B16F10 cells to invade the extracellular matrix was analyzed in Boyden chambers equipped with matrigel coated filters (2 × 105 cells/chamber, 4 h incubation). Histogram represents the arithmetic mean values of the number of invading cells/field ± SD of three independent determinations. (C) D16F7 mAb inhibits D16F10 cell migration in response to PlGF. Migration of B16F10 cells (1.5 × 105 cells/chamber) induced by PlGF (50 ng/ml, 18 h incubation) was evaluated in Boyden chambers equipped with gelatin coated filters, in the absence (No Ab) or presence of 2.5 μg/ml D16F7 mAb or control mouse IgG mAb (CTR mAb). Histogram represents the mean values of the number of migrated cells/field ± SD of three independent determinations. NS, non-stimulated. (D) Effect of D16F7 mAb on B16F10 cell ability to form tube-like structures. Cells (4 × 104/well), untreated or pre-incubated with 5 μg/ml D16F7 mAb or control mouse IgG mAb at room temperature for 30 min, were seeded in the absence or presence of 50 ng/ml VEGF-A on 24-wells plates coated with matrigel. Tube-like structures formation was analyzed after 48 h. Photographs from a representative experiment out of three are shown (×50 magnification). Histogram represents the arithmetic mean values of the number of tube-like structures ± SD, counted in ten different microscopic fields for each experimental group, for a representative experiment out of three.
