Figure 5. Effects of D16F7 mAb treatment on tumor cells in an in vivo murine model.
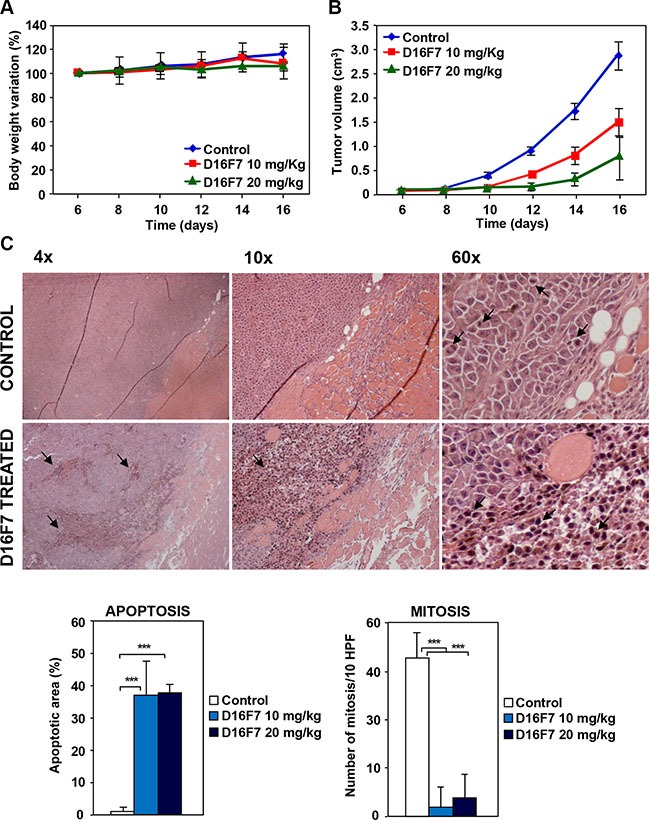
(A) Safety analysis of D16F7 treatment. Toxicity of D16F7 mAb treatment was evaluated on the basis of net body weight reduction in B6D2F1 mice treated with five doses of the indicated amounts of the antibody (8 animals/group), as compared to control animals. (B) D16F7 mAb inhibits in vivo tumor growth. B16F10 melanoma cells (2.5 × 105/mouse) were injected i.m. in the left hind limb of B6D2F1 mice (8 animals/group) and, when the tumor mass was palpable (i.e., day 6 after tumor challenge), animals were treated with vehicle (PBS) or with the indicated doses of D16F7 mAb. Tumor growth was evaluated every other day. Results are the arithmetic mean of tumor volumes ± SD. Statistical analysis using the ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test method for multiple comparisons indicated that differences in tumor size between untreated and D16F7 mAb treated mice (both 10 and 20 mg/kg doses) were statistically significant starting from day 10 onward (p < 0.05). Differences in tumor size between mice treated with 10 and 20 mg/kg of D16F7 mAb were statistically significant starting from day 12 onward (p < 0.05). Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. (C) D16F7 mAb induces apoptosis in B16F10 melanoma cells in vivo. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of histological sections of melanoma samples obtained from control or mAb treated mice. Control mice show a tumor mass composed by vital cells with brisk mitotic activity (arrows in panel 60×) and very few area of necrosis in the tumor core. Treatment with D16F7 mAb (10 mg/kg) induces a degenerative aspect of the tumor mass with a high number of apoptotic cells (arrows). Histograms represent the mean percentage ± SD of tumor mass area occupied by apoptotic cancer cells or mean number ± SD of cells/10 high-power fields (HPF) displaying mitotic activity in control and treated tumors (10 and 20 mg/kg).
