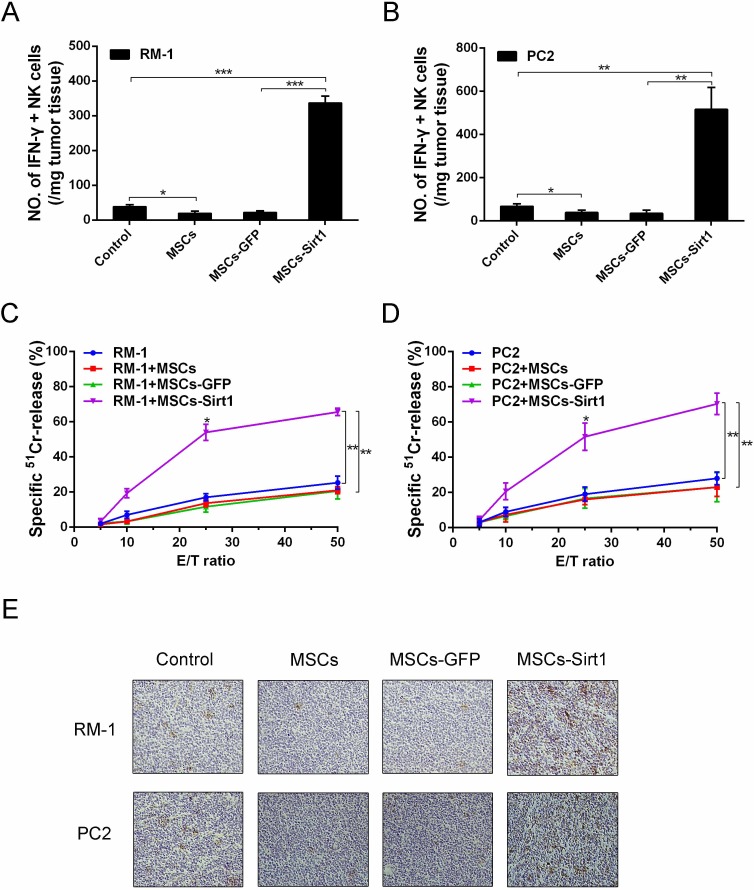
Figure 2. Tumor infiltrating NK cells evaluation in tumor-bearing mice.
Tumor infiltrating cells were isolated from A. RM-1 and B. PC2 tumor tissues, then analyzed by surface staining with anti-mouse NKp46 (eBioscience) for NK cells, followed by intracelluar IFN-γ staining. C. and D. Splenocytes (effector, E) were isolated from the mice and assayed against YAC-1 cells (target cell, T). Cell lysis was determined in triplicate and 51Cr isotope release assay at different effector-to-target cell (E/T) ratios were performed to determine the cytotoxic potential of effector populations. E. NK cells of tumor tissues were determined by immunohistochemistry assessment (original magnification: ×200). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.