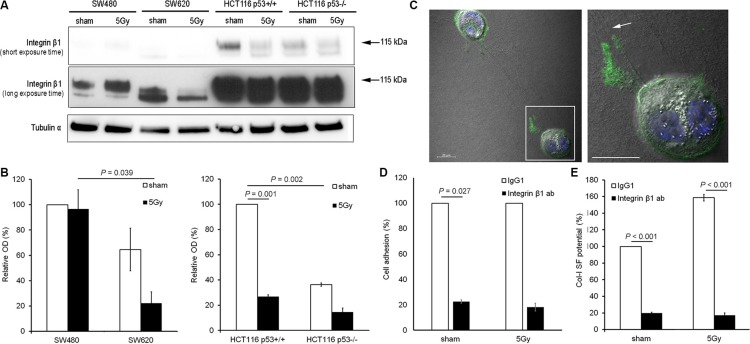
Figure 4. Integrin β1 functionality was essential for col-I adhesion and col-I SF by colon cancer cells after X-radiation.
(A and B) Representative blots (short and long exposure times) and quantitative results for integrin β1 expression in the four colon cancer cell lines for sham and 5 Gy X-radiated conditions. Hereby, the mature form of integrin β1 was quantified (arrows indicate the protein bands with molecular weight of 115 kDa). Tubulin α was used as loading control. Error bar represents the standard error of the mean (nIrExp = 3, t-test). (C) Visualization of total integrin β1 expression and col-I fiber straps formed by 5 Gy X-radiated HCT116 p53+/+ cells using confocal fluorescence microscopy and differential interference contrast microscopy, respectively (right panel shows framed area indicated in left panel; arrow indicates col-I SF at integrin β1-rich tip of cell protrusion; scale bar = 20 μm). (D) Quantification of the col-I adhesion potential of HCT116 p53+/+ cells in sham or 5 Gy irradiated condition, after control (IgG1) or neutralizing integrin β1 antibody (10 μg/mL) treatment. Error bar represents the standard error of the mean (nIrExp = 3). (E) Quantification of the col-I SF potential of HCT116 p53+/+ cells in sham or 5 Gy X-radiated condition after control (IgG1) or neutralizing integrin β1 antibody (10 μg/mL) treatment. Error bar represents the standard error of the mean (nIrExp = 3; t-test).