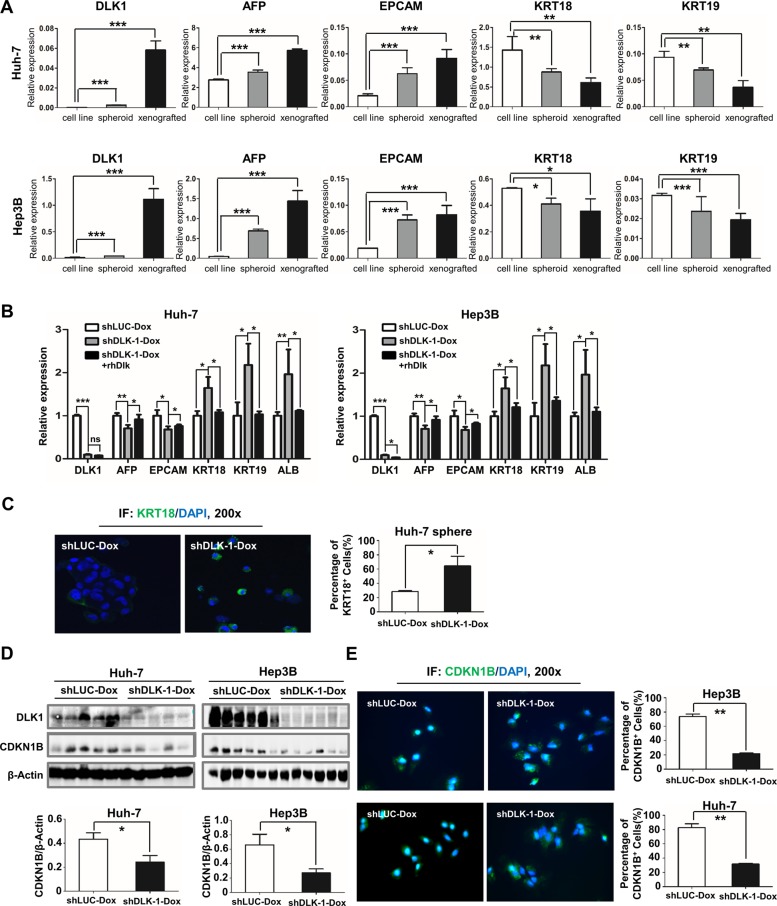
Figure 6. Inducible downregulation of DLK1 promotes cell differentiation of HCC.
(A) Molecular markers for hepatic progenitor and differentiated cells were enriched in spheroid colonies and xenograft tumors. The qRT-PCR data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. For comparison with expression level of cell line, Student's t-test was performed. (B) Decreased AFP and EPCAM as well as increased KRT18, KRT19 and ALB in spheroids were detected by quantitative RT-PCR when DLK1 was knocked down by DOX addition. The expression level of CSC markers was reversed in the regenerated spheroids as recombinant DLK1 protein was introduced to culture medium. The qRT-PCR data were also analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by pair-wise comparison. (C) Cell spheres were collected for immunofluorescent staining. KRT18+ cells were counted from three random fields (mean ± SD) (right). (D) Xenograft tumors derived from Huh-7 and Hep3B cells were examined using western blotting assay with anti-CDKN1B antibody (upper) and then CDKN1B level was normalized based on b-actin and statistically analyzed (bottom). (E) The immunofluorescence assays depicted the CDKN1B staining (green) and the cell nucleus dyed with DAPI (blue). The right histograms represent the percentage of CDKN1B+ cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.