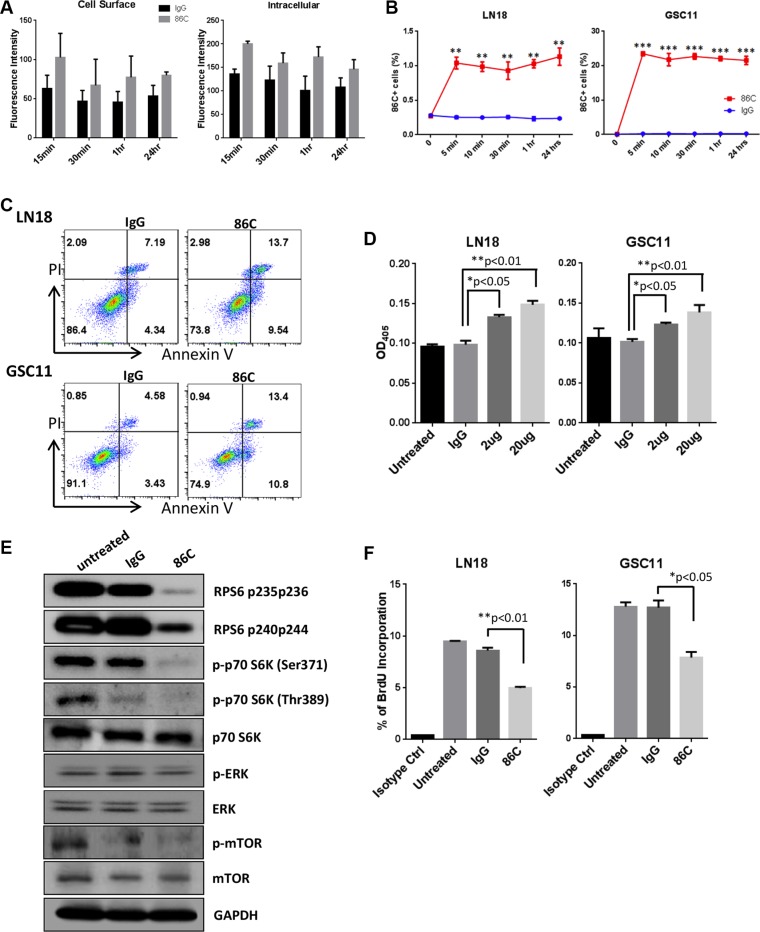
Figure 5. Rapid internalization of 86C is associated with induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation.
(A) LN18 cells were incubated with 86C for 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, or 24 hours and were fixed and permeabilized for immunofluorescent detection. The 86C in the cells was stained with Alexa Fluor 647–conjugated IgG, and total fluorescence intensity was measured at 650 nm excitation and 665 nm emission. 86C on the LN18 cell surface was also stained with Alexa Fluor 647–conjugated IgG without permeabilization. (B) Cells cultured with 86C for 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, or 24 hours were fixed using 2% paraformaldehyde. After fixation, cells permeabilized were stained with Alexa Fluor 405–conjugated anti-mouse IgG to trace 86C in the cells and analyzed using flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). **P < 0.01 or ***p < 0.005 versus IgG treatment. Student t test. (C) LN18 and GSC11 cells were treated with 2 μg/ml IgG or 86C for 24 hours. Then, single-cell suspensions were stained with Annexin V and propidium iodide to determine proportions of necrotic and apoptotic cells by flow cytometry. (D) Caspase-3 assay of LN18 and GSC11 cells treated with different concentrations of 86C. The reduction in cell viability correlated with an increase in caspase-3 activity, which was statistically significant at 2 μg/ml (P < 0.05). (E) LN18 and GSC11 cells were treated with 10 μg/ml 86C for 24 hours. Cells were subjected to lysis, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting to detect phosphor-RPS6, phosphor-p70S6K, p70S6K, phosphor-ERK, ERK, phosphor-mTOR, and mTOR. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (F) BrdU at 10 μM was incorporated into LN18 and GSC11 cells treated with 10 μg/ml 86C for 2 hours. Incorporated BrdU was stained and analyzed using flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). *P < 0.05 versus IgG treatment. Student t test.