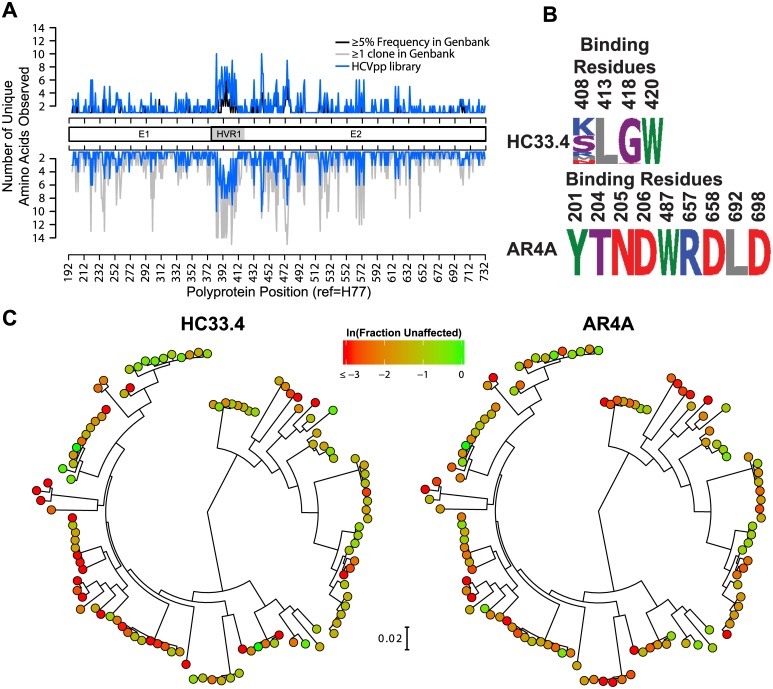
Fig 1. Construction of an HCV E1E2 panel for neutralizing antibody breadth testing and sequence prediction of neutralizing antibody resistance polymorphisms.
(A) Number of different amino acids present at each position in the 113 variant E1E2 panel (blue line). Regions spanning E1, hypervariable region 1 (HVR1), and E2 are indicated. For comparison, black line in the upper plot shows the number amino acids represented at each position by at least 5% of the sequences in a reference panel of 643 HCV genotype 1 isolates from GenBank. Gray line in the lower plot shows the number amino acids represented at each position by at least one sequence in the reference panel of 634 HCV genotype 1 isolates from GenBank. (B) Variation in the E1E2 panel of known critical binding residues for HC33.4 and AR4A. Numbers indicate the polyprotein position of each amino acid. Height of each amino acid is proportional to its frequency in the panel. Letters are standard IUPAC amino acid abbreviations. (C) Phylogenetic tree of E1E2 amino acid sequences of the 113 variant panel, determined by maximum likelihood, shown with the distances drawn to scale. Clones are colored according to their sensitivity to neutralization: ln(Fraction Unaffected (Fu) by 10 μg/mL of HC33.4 (left) and AR4A (right)). Fu is infection in the presence of 10 μg/mL of bNAb/infection in the presence of nonspecific human IgG.