Figure 1. Crosstalk between BER and DSB repair after irradiation.
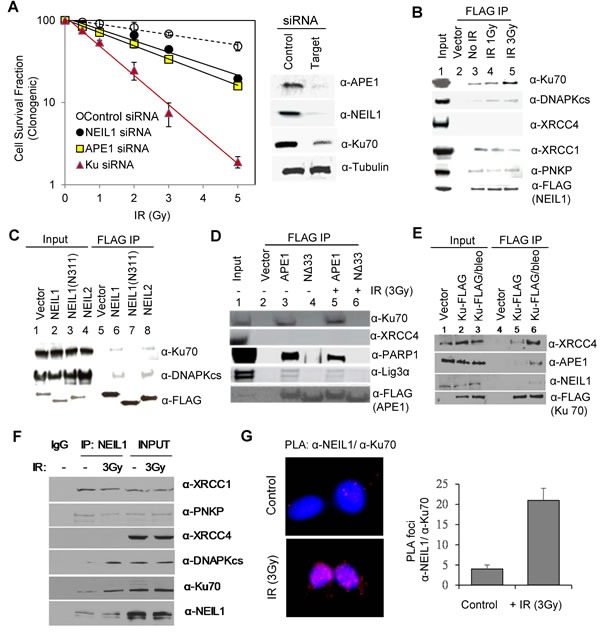
A. Loss of APE1 or NEIL1 causes moderate radiosensitization. For clonogenic survival analysis (left panel), HEK293 cells were irradiated at 48 h after transfection with siRNAs. Immunoblotting (right panel) shows depletion of target proteins. B. The FLAG-NEIL1 co-IP in HEK293 cells revealed radiation-associated increase in association of Ku, DNA-PKcs, and PNKP but not of XRCC4 with NEIL1. C. The IP of WT APE1 but not of the NΔ33 mutant (lacking APE1's common interaction domain) contained Ku and BER/SSBR proteins, The FLAG IPs were isolated from HEK293 cells after transfection with FLAG-tagged WT APE1 or the NΔ33 mutant. D. The FLAG-NEIL1/2 IP contained DNA-PKcs and Ku, but the IP of NEIL1(N311) mutant that lacks the common interaction domain (aa312-389) did not contain DNA-PKcs or Ku, underscoring the specificity of Ku interaction. E. The FLAG-Ku IP contained XRCC4, APE1, and NEIL1, whose levels increased after bleomycin treatment. F. Endogenous NEIL1 co-IP contains Ku70, DNA-PKcs after irradiation, unlike PNKP and XRCC1, which are constitutively associated. G. PLA analysis confirms in-cell association of NEIL1 with Ku, which was enhanced after IR treatment (> 25 cells were counted for the bar graph).
