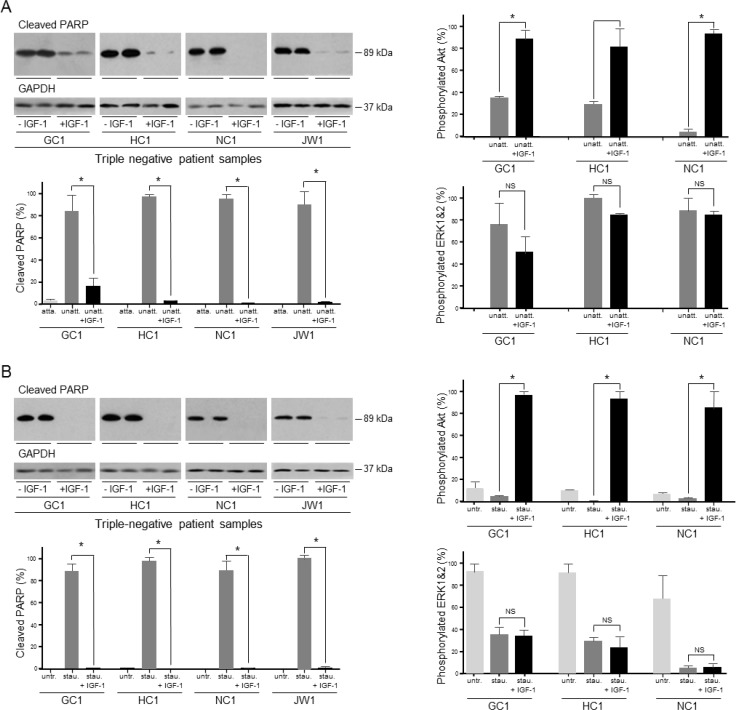
Figure 7. Role of IGF signal transduction in the survival of gastric cancer patient samples induced to undergo anoikis or apoptosis.
GC1, HC1, NC1 and JW1 cells were grown in poly-HEMA-coated wells, in the absence or presence of 50 ngml−1 IGF-1 for 24 h (GC1 and HC1) or 6 h (NC1 and JW1) A. Cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 0.5 μM staurosporine (GC1, HC1 and JW1) or 1 μM staurosporine (NC1), in the absence or presence of 50 ngml−1 IGF-1 for 5 h B. Cells were lysed and cleaved PARP, GAPDH, phosphorylated Akt, ERK1 and ERK2 were measured. Asterisks indicate levels that are statistically significantly lower or higher in the presence of IGF-1 than in its absence (One-way ANOVA; for anoikis GC1; cleaved PARP, p < 0.0001, pAkt, p < 0.001, HC1; cleaved PARP, p = 0.0003, NC1, cleaved PARP, p < 0.0011, pAkt, p = 0.0003; JW1, cleaved PARP, p < 0.0004; for apoptosis; GC1; cleaved PARP, p < 0.0001, pAkt, p < 0.001, HC1; cleaved PARP, p < 0.0001, pAkt, p < 0.0001, NC1, cleaved PARP, p < 0.0001, pAkt, p = 0.0033; JW1, cleaved PARP, p < 0.0001). NS indicates values that are not significantly different.