Figure 3. CD44v6 and matrix protein adhesion.
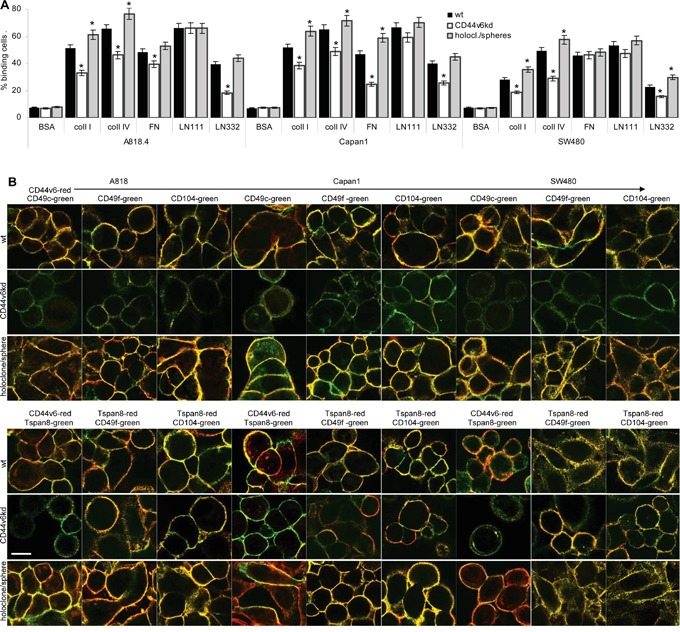
A. A818.4, Capan1 and SW480 wt, CD44v6kd and holoclone/sphere cell were seeded on matrix protein-coated plates. After 2h at 37°C, 5%CO2, non-adherent cells were removed by vigorous washing. Adherent cells were stained with crystal violet and lysed measuring OD595nm (mean±SD of triplicates). The percent of adherent cells is shown; significant differences between wt and CD44v6kd or sphere/holoclone cells: *. B. Colocalization of CD44v6 with Tspan8 and colocalization of CD44v6 and Tspan8 with integrins was evaluated by confocal microscopy in wt, CD44v6kd and holoclone/sphere cells; overlays of green fluorescence (Tspan8) and red fluorescence (CD44v6) or green fluorescence (integrins) and red fluorescence (CD44v6 / Tspan8) are shown (scale bar: 10μm). Adhesion to coll I, coll IV and LN332 is strongly reduced in A818.4-, Capan1- and SW480-CD44v6kd cells. Adhesion to LN111 is not affected and adhesion to FN mostly in Capan1-CD44v6kd cells. CD44v6 and Tspan8 colocalize with CD49c, CD49f and CD104. Reduced adhesion of CD44v6kd cells corresponds to reduced colocalization and pronounced colocalization of spheres/holoclones corresponds to stronger adhesion.
