Figure 1. Identification of Bisindolylmaleimide IX as a genotoxic agent and a topoisomerase inhibitor.
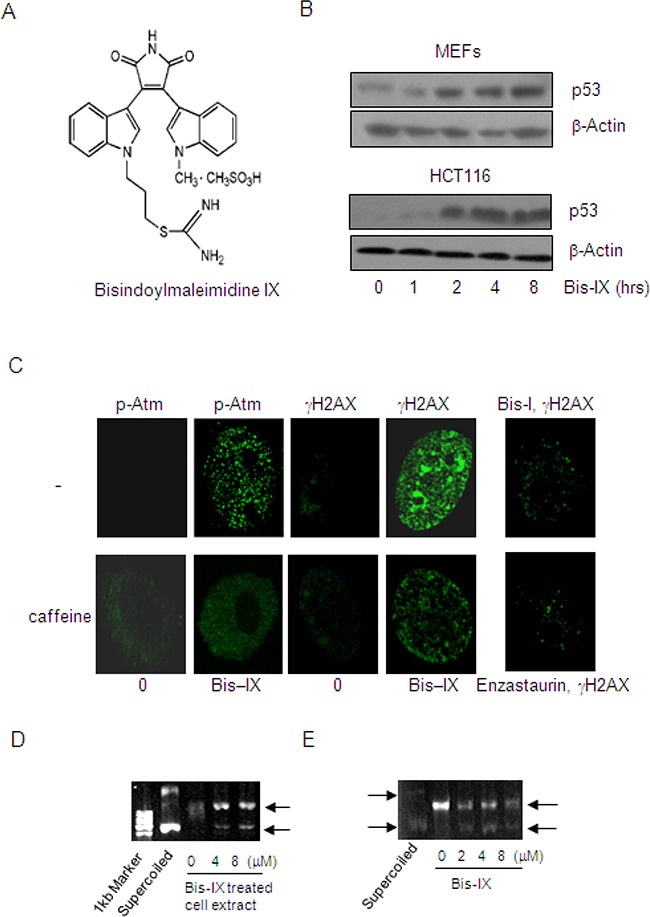
A. The structures of Bisindolylmaleimide IX. B. Bisindolylmaleimide IX induced p53 expression in MEFs and HCT116 cells. Upper panel: primary MEFs were treated with 2.5 μM Bisindolylmaleimide IX for different periods of time and the cells were collected. The levels of p53 were determined by western blot. Bottom panel: HCT116 cells were treated with 2.5 μM Bisindolylmaleimide IX for different periods of time and the cells were collected. The levels of p53 were determined by western blot. C. Bisindolylmaleimide IX induced formation of DNA damage foci for γH2AX and p-Atm in MEFs. Primary MEFs were pretreated with caffeine or solvent for 2 hrs and then with 2.5 μM of Bisindolylmaleimide IX, Bisindolylmaleimide I, or Enzastaurin for 4 more hrs. γH2AX and p-Atm were detected with immunofluorescent staining using specific antibodies. D. Bisindolylmaleimide IX inhibited the topoisomerase activity assayed with pBluescript. DNA samples of pBluescript were incubated with cell lysates of MEFs, which were treated with 0, 4 or 8 μM Bisindolylmaleimide IX before being harvested. DNA samples were analyzed on agarose gels. E. Bisindolylmaleimide IX directly inhibited the topoisomerase activity in vitro assays. DNA samples of pBluescript were incubated with cell lysates of BaF3 in the presence of 0, 2, 4 or 8 μM Bisindolylmaleimide IX. DNA samples were analyzed on agarose gels.
