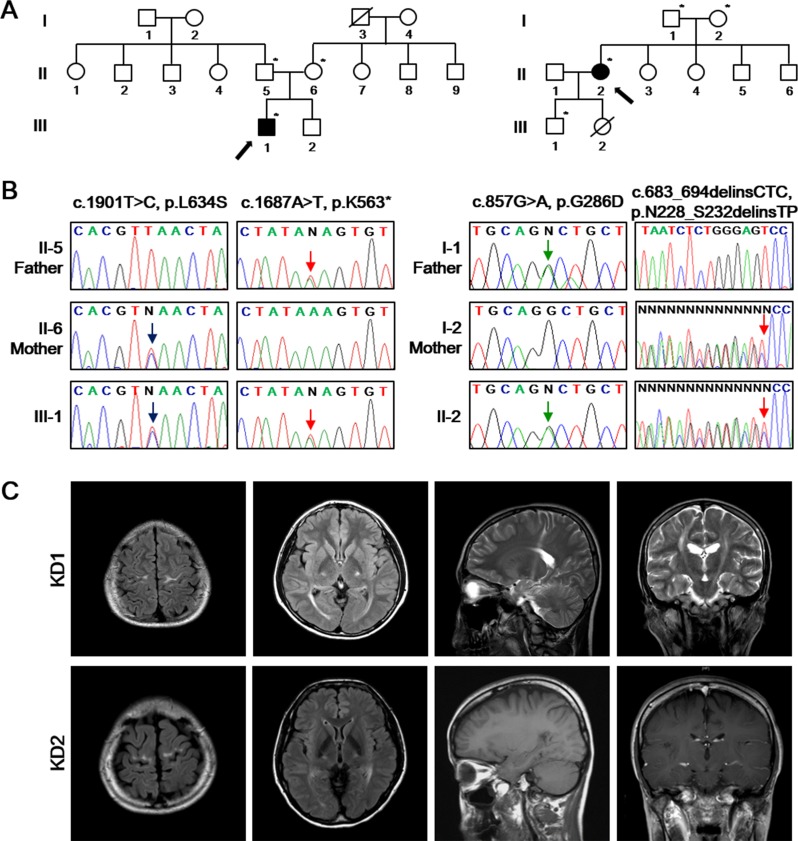
Figure 1. Identification of the disease-causing mutations of GALC in two unrelated families.
A. Pedigrees of two KD patients (left: KD1; right: KD2) with GALC mutations. The available DNA samples are indicated by asterisks (*). The probands are marked with arrows with filled symbols. Hashed symbols indicate deceased individuals. B. Sanger sequencing of the GALC gene (Reference mRNA sequence: NM_000153.3) from the patients identified c.1901T>C (p.L634S) combined with c.1687A>T (p.K563*) (left) and c.857G>A (p.G286D) combined with c.683_694delinsCTC (p.N228_S232delinsTP) (right). C. Brain MR images of KD1 patient revealed the severe high intensity signal of the precentral gyrus, corona radiata, posterior limb of internal capsule, cerebral peduncle of the bilateral pyramidal tracts and optic radiation on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and T2-weighted images. Brain MRI of the patient KD2 revealed the high intensity signal in the precentral gyrus and posterior limb of internal capsule, without signal abnormality on the T1-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images.