Figure 3. iNOS−/− effector DCs induce enhanced CD4+ T cell activation.
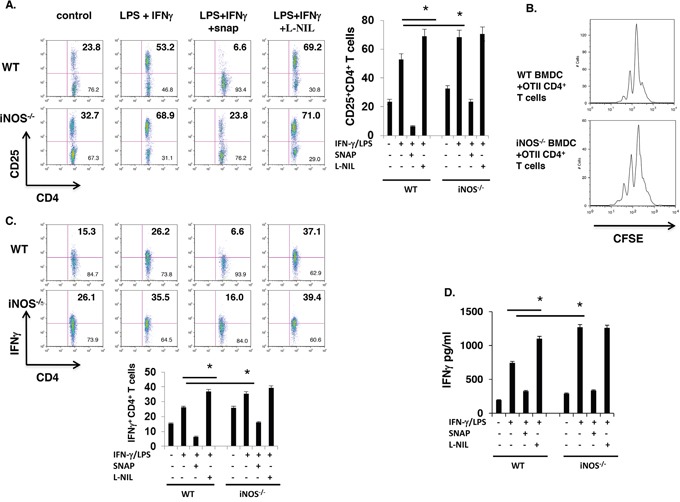
A. Bone marrow cells from WT and iNOS−/− mice were cultured with GM-CSF (10ng/ml) and IL-4 (10ng/ml) for 7 days, then stimulated with IFN-γ (10ng/ml) plus LPS (100ng/ml) for 24 h, then BMDCs were thoroughly washed with medium and were irradiated with 2000 rad, CD4+ T cells purified from spleen and lymph nodes of OTII transgenic mice were co-incubated with these WT or iNOS−/− BMDCs for 3 days in present of OTII peptide. CD25 expression on T cells as activated markers were stained by FACS. B. BMDCs were prepared as in (A) and CD4+ T cells purified from spleen and lymph nodes of OTII transgenic mice and then were labelled with CFSE as indicating T cells proliferation status, CFSE labelled T cells were co-incubated with irradiated WT or iNOS−/− BMDCs for 3 days in present of OTII peptide, proliferation of CD4+ T cells was analyzed by FACS. C. BMDCs and CD4+ T cells were prepared in (A) and were co-incubated with irradiated WT or iNOS−/− BMDCs for 3 days in present of OTII peptide, then stained for intracellular IFN-γ in CD4+ T cells by flow cytometry. D. IFN-γ production in the supernatants prepared in (A) was analyzed by ELISA. Data represent mean ± SD. * P<0.05. **P<0.01.
