Figure 6. Absence of APE1 acetylation leads to accumulation of AP sites in the genome and sensitizes cells to DNA damaging agents.
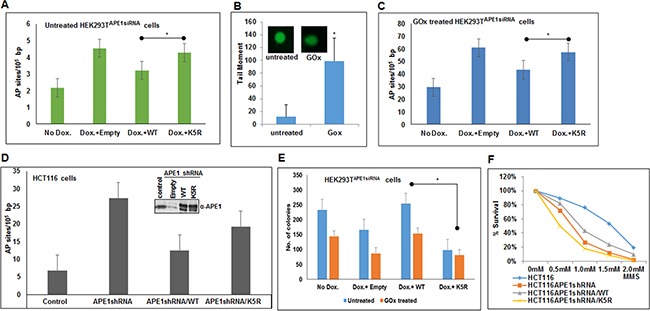
A & C. Endogenous APE1 was downregulated in HEK293TAPE1siRNA cells with Dox treatment. FLAG-tagged WT or acetylation defective (mutations of Lys 6, 7, 27, 31 & 32 to non-acetylable Arg; K5R) mutant APE1 was ectopically expressed in these cells. AP sites in the genomic DNA were measured using ARP kit in glucose oxidase (GOx; 100 ng/ml for 30 mins) treated (C) or untreated control (A) cells. Bar diagram representing number of AP site/105 bp. Error bars indicate mean ±SD (n=3). B. FPG Comet assay to assess relative quantitation of oxidative DNA damage after GOx treatment. Histogram showing mean tail moment (50-100 randomly selected cells) after GOx treatment; representative images of Comet slides shown in inset. D. Quantitation of AP sites in control, APE1 shRNA expressing HCT116 cells, WT or K5R mutant APE1 expressing HCT116 cells after endogenous APE1 downregulation (expression level shown in inset) as in A & C. E & F. DNA damage cell sensitivity assay measured by clonogenic assay (E) after GOx treatment in endogenous APE1 downregulated HEK293TAPE1siRNA cells (by Dox treatment) and after ectopic expression of WT or K5R mutant APE1in endogenous APE1 downregulated cells, and (F) in APE1 shRNA expressing HCT116 cells transfected with WT or K5R APE1 and treated with different dose of MMS and plotted as % survival. Details are in Materials and Methods. * represents p value < 0.05 (Student T Test).
