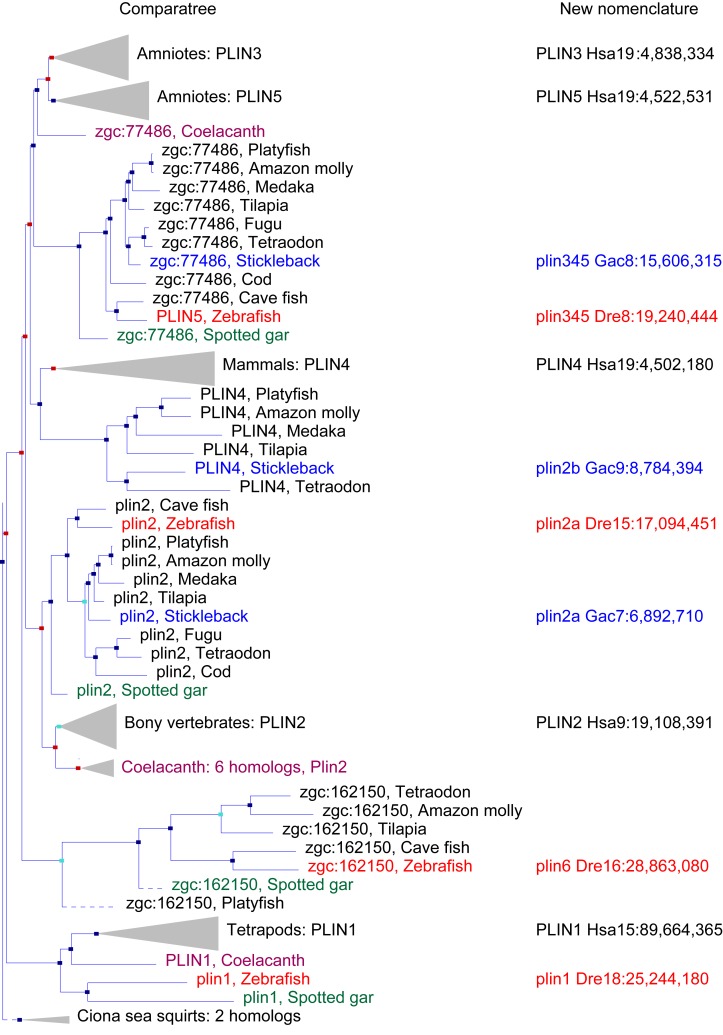
(
A, D) The region of human (
Homo sapiens) chromosome 9 (Hsa9) containing
PLIN2. (
B) The region of stickleback linkage group 7 (Gac7) containing
plin2a. (
C) The region of Gac9 containing
plin2b. Compara Gene Tree analysis suggested that stickleback (
Gasterosteus aculeatus) has an ortholog (ENSGACG00000017870) of the human
PLIN4 gene. Given the absence of a
PLIN4 ortholog in non-mammalian lobefins, we examined this conclusion in more detail by performing conserved synteny analysis using the Synteny Database (
Catchen et al., 2009,
2011b). Analysis showed that the chromosome segment containing ENSGACG00000017870 shares conserved syntenies with the region of Hsa9 that contains
PLIN2, not the region on Hsa19 that contains
PLIN4. Further analysis showed that the region of Gac9 that contains ENSGACG00000017870 shares many paralogs with the region of Gac7 that contains what Ensembl calls
plin2 (ENSGACG00000019638), for example, ‘
LGI(2of2) and LGI(1of2), CCDC145(2of2) and CCDC145(1of2),
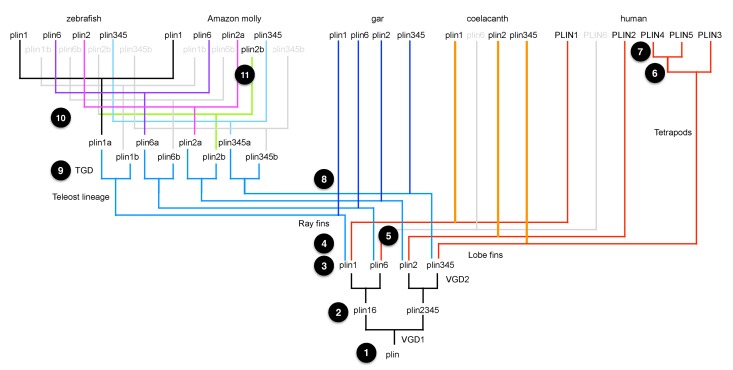
MYOZ2(1of2) and MYOZ2(2of2)' and others. We conclude that these two chromosome segments originated in the teleost genome duplication (TGD) event (
Amores and Force, 1998;
Postlethwait et al., 1999;
Taylor et al., 2003;
Jaillon et al., 2004a) and that the percomorph clade labeled ‘PLIN4’ by Compara Gene Tree is actually a TGD duplicate of human
PLIN2. Under this interpretation, ancestral teleosts had
plin2a and
plin2b genes and that
plin2b was lost in ostariophysans, including zebrafish and blind cavefish (
Asyanax mexicanum).