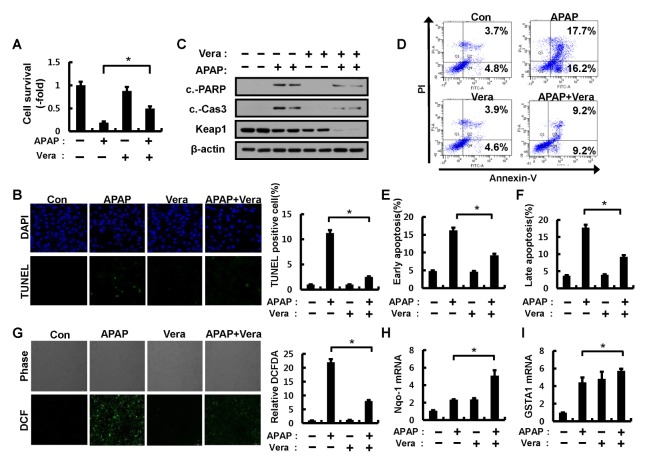
Fig. 4.
Verapamil alleviates APAP-induced cytotoxicity via Nrf2 activation. (A) Hepa1c1c7 cells were pretreated with APAP (10 mM) for 1 h and incubated in the absence or presence of verapamil (100 μM) for 18 h. Cell viability was estimated using a Cell titer-Glo assay kit. The live cell number was expressed as the absorbance at luminescence. (B) TUNEL analysis of Hepa1c1c7 cells treated as in (A) and quantitation of TUNEL analysis. (C) Hepa1c1c7 cells treated as described in (A) were lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-3, Keap1, and β-actin (loading control). (D) Apoptosis in Hepa1c1c7 cells pretreated with APAP and incubated in the absence or presence of verapamil were detected by FACS analysis for Annexin V and PI staining. (E) Early apoptosis. (F) Late apoptosis. (G) ROS levels were determined using CM-H2DCFH-DA. Representative images are shown. Quantitative analysis of cells treated as described in (A). The relative dichlorofluorescein fluorescence was calculated by averaging the levels of fluorescence from 80–100 cells after subtracting the background fluorescence obtained using a fluorescence microscope. Total RNA isolated from cells treated as described in (A) was subjected to qRT-PCR analysis for mRNAs of GSTA1 (H) and Nqo-1 (I). Data are presented as the means ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.