Figure 4.
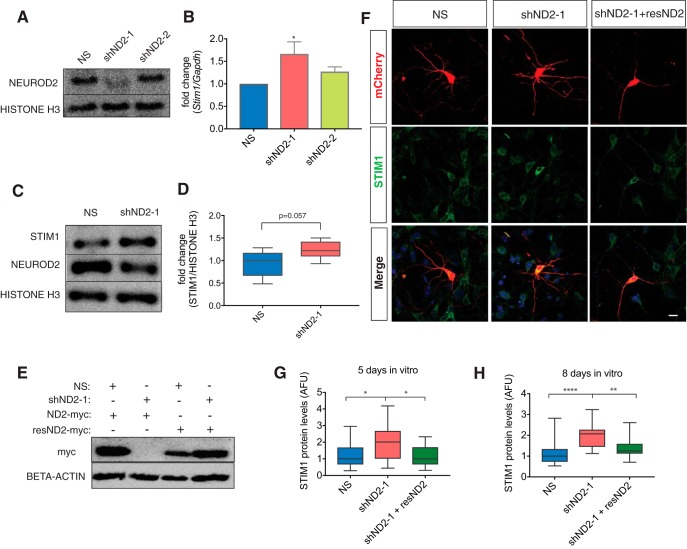
NEUROD2 suppresses Stim1 expression. A, Immunoblotting analysis reveals that two separate shRNAs (shND2-1 and shND-2) can suppress Neurod2 expression compared with a nonsilencing shRNA (NS) in primary cortical cultures with different efficiencies. B, Neurod2 mRNA levels normalized to Gapdh mRNA is measured by RT-qPCR in cortical cultures transfected with either shND2-1 or shND2-2. While both shRNAs induce an upregulation of Stim1 mRNA, the effect of the more potent shND2-1 is greater. Data represent three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test, *p = 0.023. C, D, Primary cortical cultures were transfected with NS shRNA and shND2-1. STIM1 protein levels were quantified by immunoblotting and normalized to histone H3 loading control. Data are presented as bar graphs; the line marks the median; the box represents the 25th and 75th percentiles; top and bottom whiskers mark minima and maxima, respectively. Unpaired t test, p = 0.057. E, resND2-myc, a cDNA resistant to shND2-1, was generated. HEK293T cells were transfected with NS shRNA or shND2-1, along with either ND2-myc or resND2-myc cDNAs. Immunoblotting analysis against the myc epitope revealed that while shND2-1 completely knocked down the expression of ND2-myc, resND2-myc expression was not affected. F, Primary cortical neurons were transfected at low efficiency with shND2-1 either alone or together with resND2-myc and immunofluorescently stained against STIM1 protein. Transfected cells were identified based on their coexpression of mCherry from the shRNA-expressing plasmid. G, H, Quantification of STIM1 immunofluorescence signals from experiments presented in F. Experimenter was blinded to all sample identity during staining and quantification. n = 30 for each condition from two independent experiments. Scale bar, 20 µm. Data are presented as bar graphs; the line marks the median; the box represents the 25th and 75th percentiles; top and bottom whiskers mark minima and maxima, respectively. Nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test was followed by Dunn’s multiple-comparison analysis, *p < 0.02, **p = 0.0012, ****p < 0.0001 (Table 2).