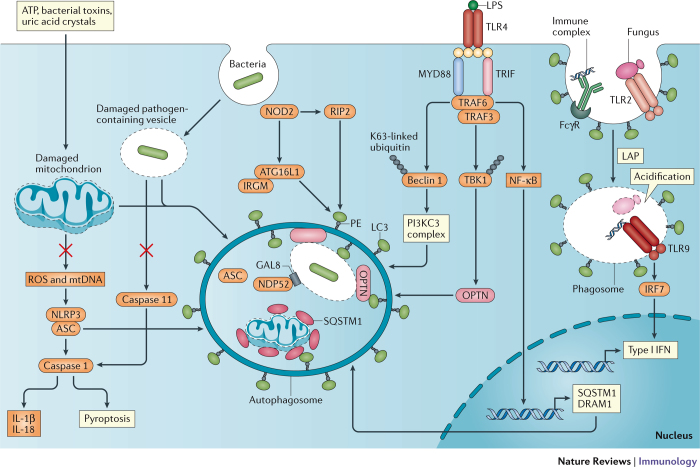
Figure 1. Crosstalk between Toll-like receptor and NOD-like receptor signalling and autophagy.
Exposure to exogenous agents including ATP, bacterial toxins and uric acid crystals damages mitochondria, which results in the release of factors such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) that activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Autophagy inhibits inflammasome activation by sequestering damaged mitochondria and the NLRP3-binding protein ASC to prevent caspase 1-mediated cleavage of pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β) and pro-IL-18 into the active forms, as well as to prevent pyroptosis. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2 (NOD2) in the cytosol recognizes bacterial peptidoglycan and viral RNA from internalized pathogens and subsequently induces autophagy, either by signalling through receptor-interacting protein 2 (RIP2) or by directly recruiting ATG16L1 in a complex with immunity-related GTPase family M protein (IRGM). Incorporation of the bacteria into the autophagosome is achieved by LC3-binding proteins, such as sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), optineurin (OPTN) and NDP52, which recognize the damaged vacuole or mitochondrion tagged by ubiquitin and galectin 8 (GAL8). In addition to inhibiting pathogen replication, this process reduces leakage of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into the cytosol to prevent activation of the caspase 11 inflammasome. Following LPS-mediated activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation primary-response protein 88 (MYD88) and TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFNβ (TRIF) signal through TNFR-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and TRAF3 to facilitate autophagy by inducing the K63-linked ubiquitylation and release of beclin 1 from inhibition, through the phosphorylation and activation of OPTN through TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) ubiquitylation, and by inducing nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling and transcription of SQSTM1 and the autophagosome maturation protein DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator protein 1 (DRAM1). Recognition of internalized fungal glycans and immune complexes by TLR2 and the Fcγ receptor (FcγR) triggers LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP). As the phagosome acidifies, the fungal pathogen is degraded and activates TLR9 to induce signals through interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) and type I interferon (IFN) transcription. PI3KC3, phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit type III.