Fig. 1.
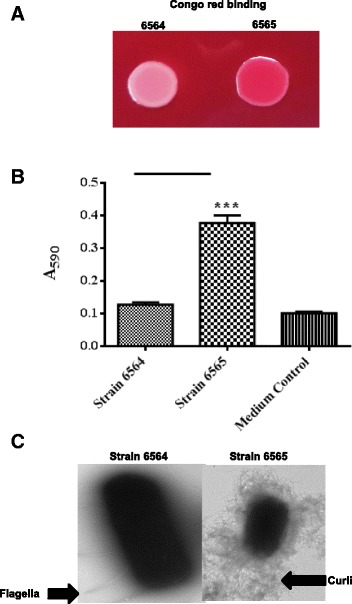
Congo red binding, biofilm production and cell surface expression of curli fimbriae by CR− parental (NADC 6564) and CR+ mutant (NADC 6565) isolates. a Color photograph showing difference in the ability of CR− and CR+ isolates to bind Congo red after 48 h of growth at 28 °C on YESCA agar containing Congo red. b Quantitative analysis of the amount of biofilms produced by strains NADC 6564 and NADC 6565 after 48 h of growth. The amount of biofilms produced was inferred from the amount of crystal violet bound by the heat-fixed biofilms. Bars represent the means of three independent assays and error bars represent standard deviation of 2. The * above the bars indicates p < 0.05 when NADC 6565 was compared to the parental strain NADC 6564. c Transmission electron micrographs of glutaraldehyde-fixed bacterial cells for detection of cell surface curli fimbriae in NADC 6564 and NADC 6565. Dark-stained structures represent bacterial cells and curli fimbriae appear as hair like structures (indicated by an arrow) on dark-stained cells. The bacterial cells were photographed at different magnifications to capture differences in the presence of curli at their cell surfaces. The strains otherwise have similar bacterial cell sizes
