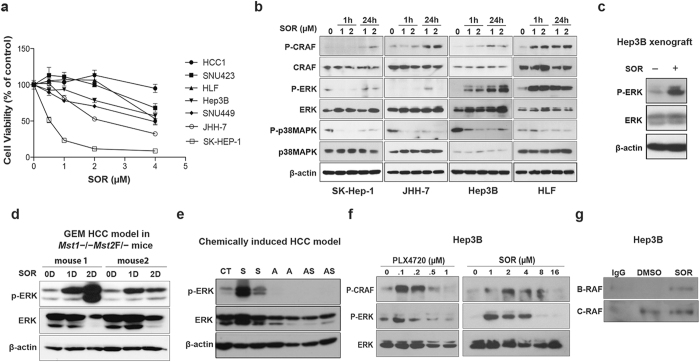
Figure 1. Paradoxical activation of ERK occurs after sorafenib treatment in BRAFWT HCC cells.
(a) In vitro sensitivity of human and murine HCC cells to clinically relevant doses of sorafenib: The IC50 values indicate that JHH-7 and SK-Hep-1 cells are more sensitive (2.26 μM and 0.5 μM, respectively), while most human HCC cell lines are quite resistant (IC50 of 6.4 μM for SNU-423 cells; 4.75 μM for HLF cells; 4.70 μM for Hep3B cells; 3.82 μM for SNU-449 cells). Similarly, murine HCC1 cells are resistant to sorafenib at these doses (n = 6). (b) Rapid CRAF and ERK activation in BRAFWT HCC cells but not in BRAFV600 HCC cells (SK-Hep-1) after sorafenib treatment. All human and murine HCC cell lines tested showed down-regulation of p38MAPK activity after sorafenib treatment. (c) Sorafenib treatment increased ERK activity in orthotopic xenograft HCCs. (d) Spontaneously arising HCCs in Mst1−/−Mst2Flox/- transgenic mice (e) and chemically induced HCCs in mice treated with CCl4 for 28 weeks. (f) CRAF and ERK activation is rapid in Hep3B cells after exposure to PLX4720 and sorafenib. (g) Transactivation of RAF dimers occurred in Hep3B cells (HCC-1 cells) treated with 2 uM sorafenib for 1 h.