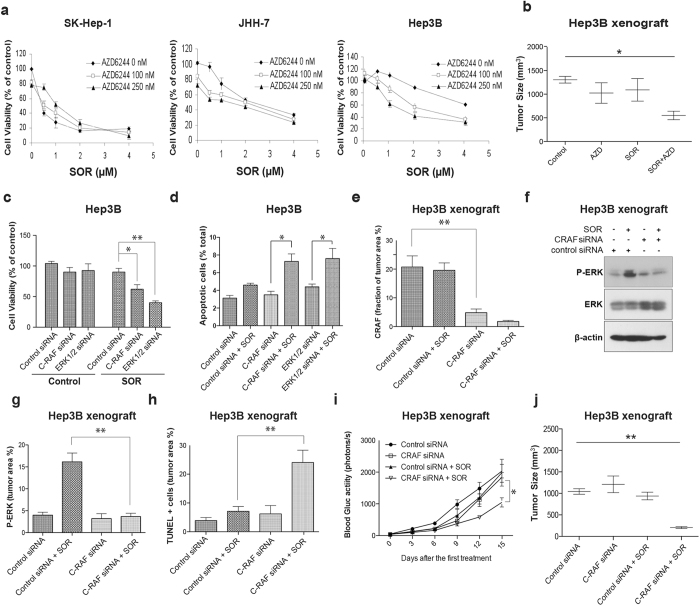
Figure 2. Paradoxical activation of ERK promotes sorafenib resistance in BRAFWT HCC cells.
(a) Effect of MEK inhibition on cell sensitivity to sorafenib: Sorafenib and AZD6244 show comparable cytotoxicity and no additive effects against SK-Hep-1 BRAFV600 mutant HCC cells. Inhibition of ERK activity with a pharmacologic MEK inhibitor (AZD6244) renders Hep3B and HLF cells sensitive to sorafenib. (n = 6). (b) Treatment with combination of sorafenib and AZD6244 resulted in synergistic tumor growth delay (n = 4). (c) Combination of sorafenib with CRAF or ERK siRNA leads to a synergistic cytotoxic effect in Hep3B cells. (d) Combination of sorafenib with CRAF or ERK siRNA increases apoptosis in Hep3B cells. Combination of sorafenib with CRAF siRNA encapsulated in liposome-based nanoparticles silenced CRAF expression (e), downregulated ERK activation (f,g) and increased cell apoptosis (h) in orthotopic Hep3B xenografts in nude mice, which resulted in synergistic tumor growth delay, as estimated by blood Gluc measurements (i) and tumor size (j). The data are the mean value ± S.E.M., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.