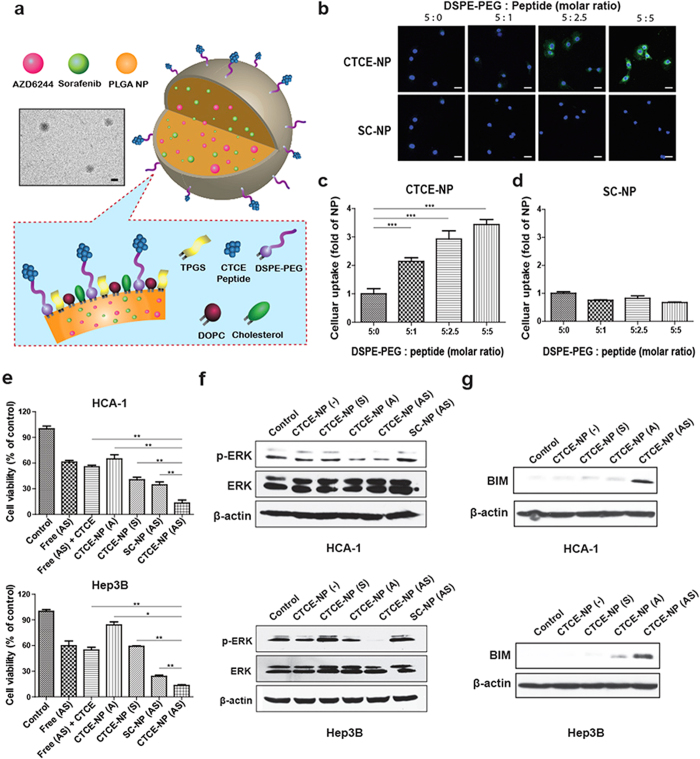
Figure 4. The NPs modified with CTCE peptides enhanced cellular uptake in HCC cells, exerted potent cytotoxic effects and prevented the paradoxical activation of ERK when loaded with sorafenib and the MEK inhibitor AZD6244.
(a) Structures proposed for the CTCE-NPs with a representative TEM image (Scale bar = 100 nm). (b–d) Murine HCC cells (HCA-1 cells) were treated with C6-loaded NPs modified with CTCE peptides (CTCE-NPs) or scramble peptides (SC-NPs) at various ratio of DSPE-PEG/peptides for 4 hr. The cellular uptake of NPs was imaged and quantified with a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope. (e) The cytotoxicity of sorafenib or AZD6244 (1 μM) in different formulations to HCC cells was measured using the MTT assay 48 hours after drug exposure (n = 4–6). (f) CTCE-NPs co-delivering sorafenib and AZD6244 prevented the effect of sorafenib on paradoxical activation of ERK in HCC cells. (g) CTCE-NPs loaded with sorafenib and the AZD6244 (0.25 μM) upregulated expression of Bim in HCC cells 24 hours after drug exposure. Scale bar = 50 μm. Free (AS), free-from AZD6244 and sorafenib; CTCE-NP (−), empty NPs modified with CTCE peptides; CTCE-NP (A), CTCE-NPs loaded with AZD6244; CTCE-NP (S), CTCE-NPs loaded with sorafenib; SC-NP (AS), AZD6244 and sorafenib loaded in NPs modified with scramble peptides.