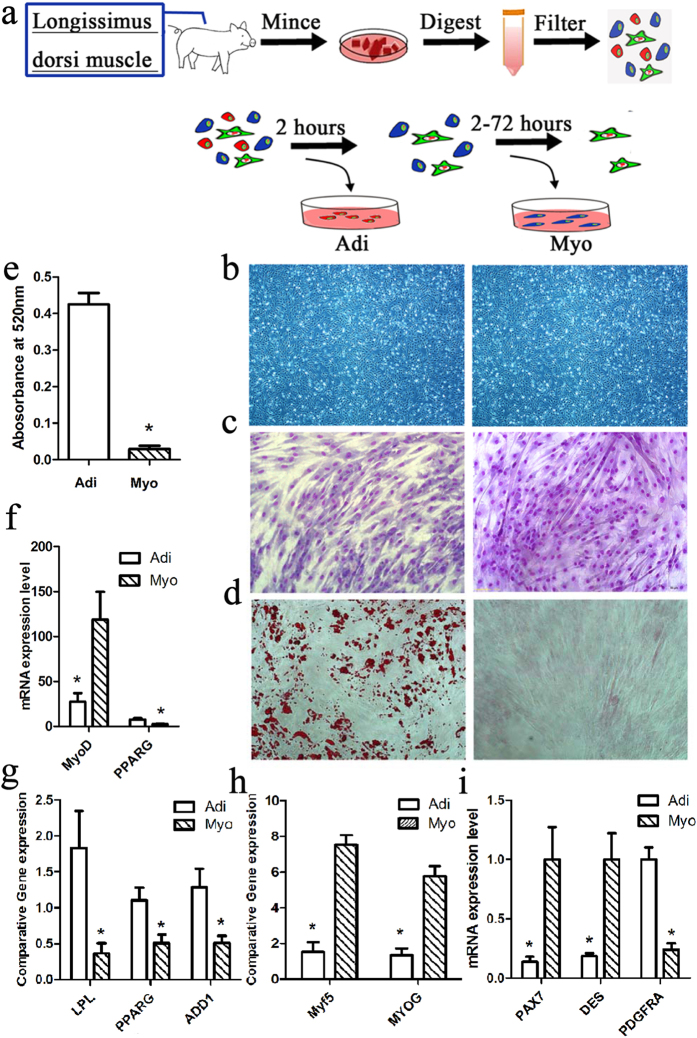
Figure 1. Isolation and identification of adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells from porcine skeletal muscle by preplate technique.
(a) Procedure of isolating adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells. (b) Morphology of adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells at passage 3, the magnification of microscope is (4 * 10). (c) porcine skeletal muscle-derived adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells were grown on collagen-I coated dishes in in myogenesis induction medium for 5 days, cell were fixed, stained with Gimsa, the magnification of microscope is (10 * 10) (d) or in adipogenesis induction medium for 10 days, cell were fixed, stained with oil-red O, the magnification of microscope is (10 * 10). (e) Quantitative analysis of lipid droplet by oil-red O OD. Measurement of adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells that after adipogenesis induction at d10. Values are means (n = 3) ± SEM, *represent significant difference between adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells with p < 0.05. (f) Gene expression (n = 3) analysis of MyoD and PPARG in pre-induction adipogenic and myogenic cells by RNA-sequencing. (g) and (h) RT-qPCR analysis of adipogenesis- and myogenesis-related gene expression after adipogenic or myogenic induction. The data of each type cells comes from three replicates. (i) RT-qPCR analysis gene expression of myogenic markers (PAX7 and Desmin) and adipogenic marker (PDGFRα) and in pre-induction adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells. The data of each type cells comes from three replicates. The procedure of isolating adipogenic (Adi) and myogenic (Myo) cells draw by Adobe Photoshop (CS5).