Abstract
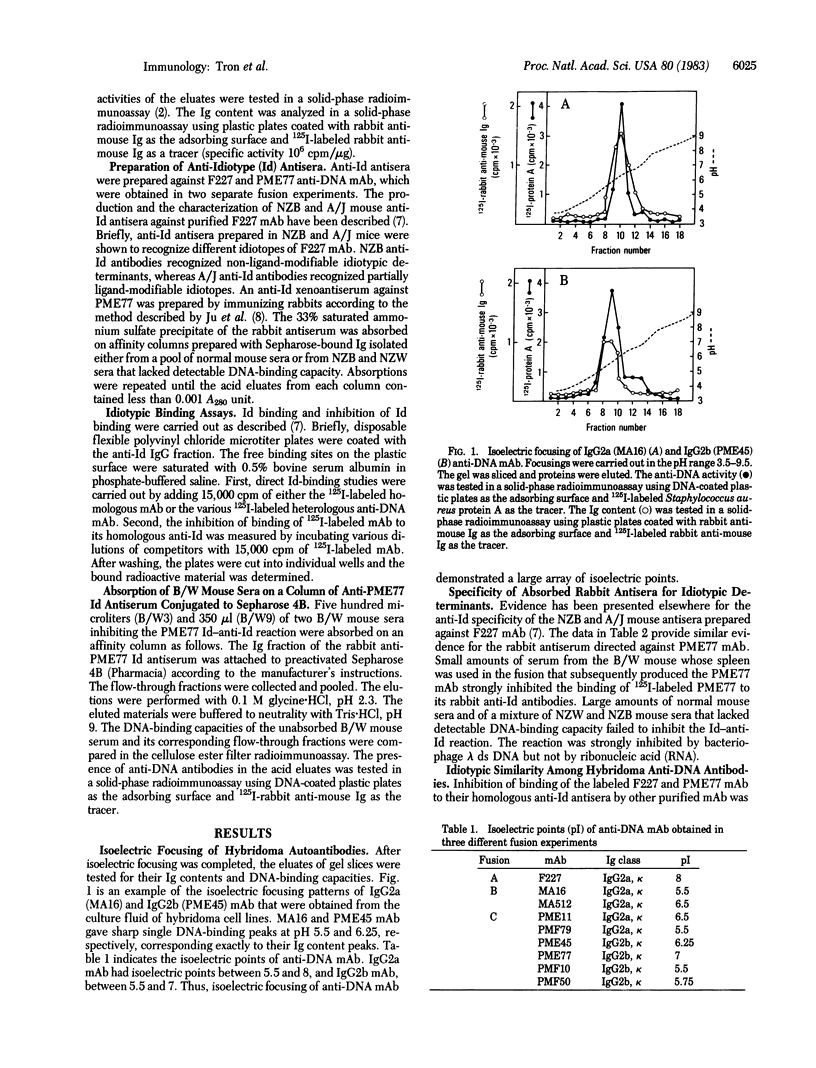
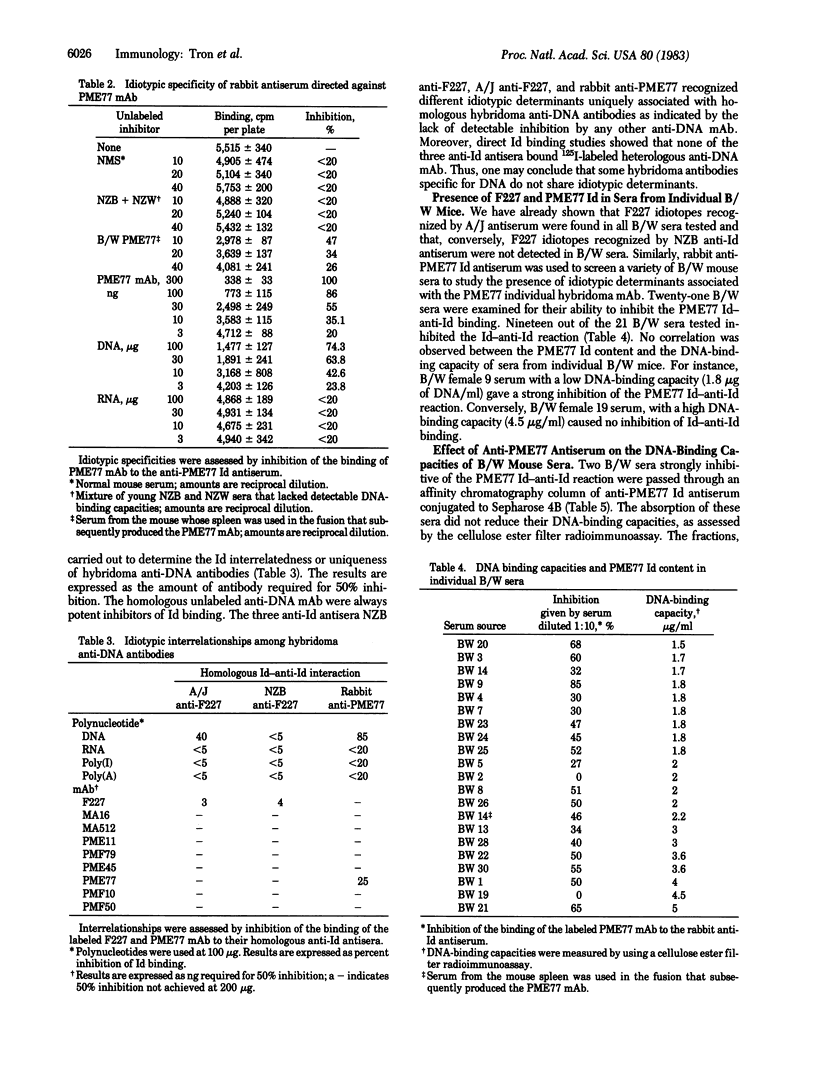
The clonal heterogeneity of nine monoclonal antibodies with absolute specificities for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was analyzed. These monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies were generated in three different fusion experiments using autoimmune (NZB X NZW)F1 mouse spleen cells. Isoelectric focusing analyses demonstrated different isoelectric points within the IgG2a and IgG2b subclasses. Three anti-idiotypic antisera were prepared (one in a rabbit and two in mice) against two monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies. These antisera detected idiotypic determinants uniquely associated with homologous hybridoma anti-DNA antibodies. Two of these idiotypes could be detected at low levels in the sera of (NZB X NZW)F1 mice. Anti-PME77 idiotypic antiserum had no effect in vitro on the total binding capacity of (NZB X NZW)F1 sera. Taken together these results demonstrate that, in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice, the anti-DNA antibody repertoire contains molecules that show similar antigen binding characteristics but are not structurally uniform.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrzejewski C., Jr, Rauch J., Lafer E., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Antigen-binding diversity and idiotypic cross-reactions among hybridoma autoantibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attias M. R., Sylvester R. A., Talal N. Filter radioimmunoassay for antibodies to reovirus RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(6):719–725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Ben Sasson S. A., Laskov R. A ribonucleic acid-specific antibody produced during autoimmune disease: evidence for nucleotide sequence specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Nov;10(11):841–845. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D. Monoclonal autoantibodies: an approach to studying autoimmune disease. Mol Immunol. 1982 Jul;19(7):943–955. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Tron F. Monoclonal anti-deoxyribonucleic antibodies. I. Isotype and specificity studies. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):895–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S., Gray A., Nisonoff A. Frequency of occurrence of idiotypes associated with anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies arising in mice immunologically suppressed with respect to a cross-reactive idiotype. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):540–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Anti-DNA autoantibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice are clonally heterogeneous, but the majority share a common idiotype. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Murphy E., Roths J. B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. A high frequency idiotypic marker of anti-DNA autoantibodies in MRL-Ipr/Ipr mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):236–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén A., Ek K., Aman P. Agarose isoelectric focusing of native human immunoglobulin M and alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90322-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Charron D., Bach J. F., Talal N. Establishment and characterization of a murine hybridoma secreting monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Le Guern C., Cazenave P. A., Bach J. F. Intrastrain recurrent idiotypes among anti-DNA antibodies of (NZB x NZW)F1 hybrid mice. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Sep;12(9):761–766. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


