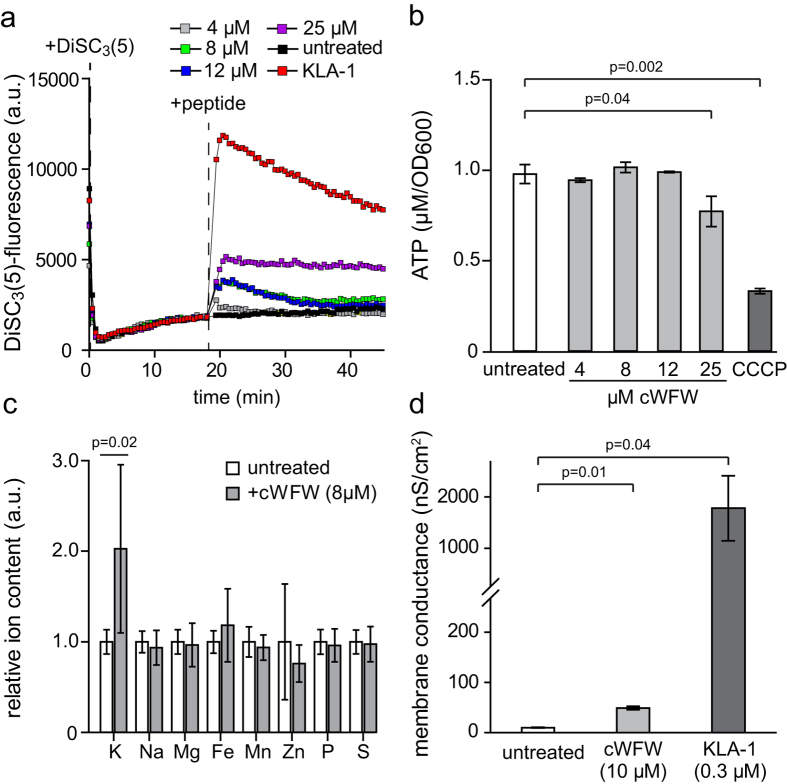
Figure 2. Impact of cWFW on cell energy state and membrane permeability.
(a) Membrane potential levels of B. subtilis upon addition of different cWFW concentrations were measured using fluorescent voltage-sensitive dye DiSC3(5). For positive control, cells were depolarised by addition of the helical pore-forming antimicrobial peptide KLA-1 (40 μM). The time points of DiSC3(5) and peptide additions are highlighted with dashed lines. See supplementary Figure 1b for growth inhibition at identical cWFW-concentrations and cell densities. The graph depicts a representative measurement of three independent replicates. (b) ATP levels in B. subtilis after 20 min incubation with different cWFW concentrations were measured using a Luciferase-based luminescence assay. For positive control, cells were incubated with the proton ionophore CCCP (100 μM). Cell densities are comparable to the data shown in panel A and supplementary Figure 1b. The diagram depicts the average and standard deviation values of three independent replicates. No significant changes (p ≥ 0.05) were observed for samples treated with 4, 8, and 12 μM cWFW. (c) Changes in relative ion content of B. subtilis upon 15 min incubation with 8 μM cWFW were determined using inductively-coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Phosphorus, mainly prevalent in DNA-bound form, served as internal control for cell mass. The diagram depicts the average and standard deviation values of three independent measurements. No significant changes (p ≥ 0.05) were observed ions other than K+. See supplementary Figure S1a for the growth inhibition of B. subtilis observed in BMM with different cWFW concentrations. (d) Conductivity measurements on planar lipid membranes formed of E. coli lipid extract upon addition of 10 μM cWFW. The pore-forming helical peptide KLA-1 (0.3 μM) served as positive control. The diagram depicts the average and standard error of two independent measurements. The statistical significances were calculated using unpaired (panels b/d) and paired (panel c) two-tailed Student t test. Strains used: (a/b) B. subtilis 168, (c) B. subtilis 168/DSM 402.