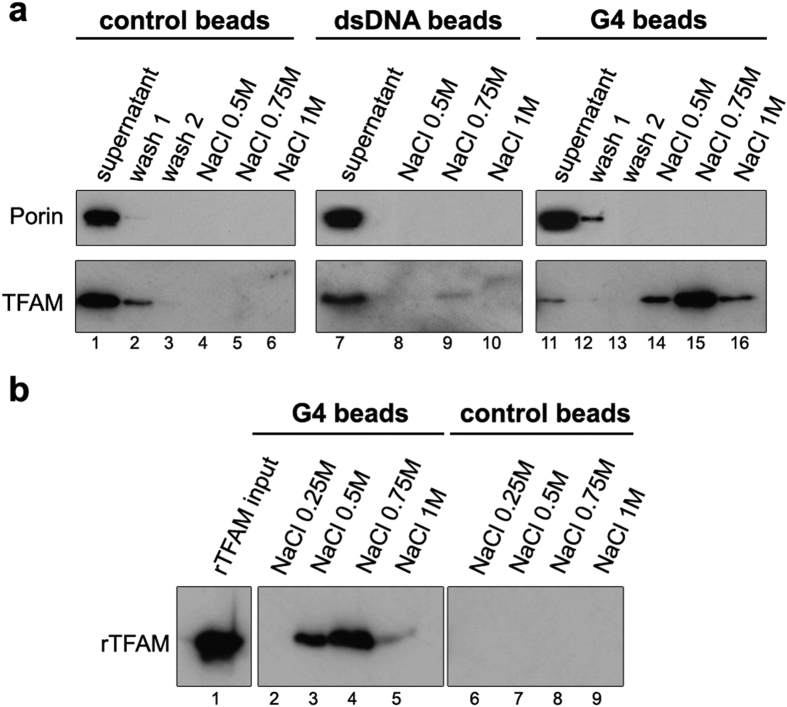
Figure 1. TFAM is captured from mitochondrial extracts with CSBII G4-DNA by pull-down assays.
Experiments were carried out with bulk magnetic beads (control beads), beads coated with CSBII DNA-G4 (G4 beads) or with the corresponding CSBII dsDNA fragment (dsDNA beads). Bound proteins were revealed by Western blot after SDS-PAGE. (a) Pull-down assays using mitochondrial fractions incubated with the indicated beads in the presence of 0.5% Triton X-100. Lane ‘Supernatant’ corresponds to the mitochondrial extract after incubation with each type of beads, and which was used as a control of the input material with Porin as a reference. The NaCl concentration at each elution step is indicated. For the naked and G4 beads, the gels show two washing steps to evince the specificity of the assay. The amounts of TFAM at the supernatants are inversely proportional to the ones eluted with NaCl. (b) Pull-down assays performed with recombinant TFAM (rTFAM) incubated with G4 (lanes 2–5) or control beads (6–9) that show non-specific binding upon blockage with appropriate buffer. Bound rTFAM was eluted with the indicated amounts of NaCl after three washings steps. Note the efficient blockage of TFAM binding to the control beads.