Fig 1. Specific recognition of V3C and V3L peptide mimotopes by V3C-type and V3L-type mAbs respectively.
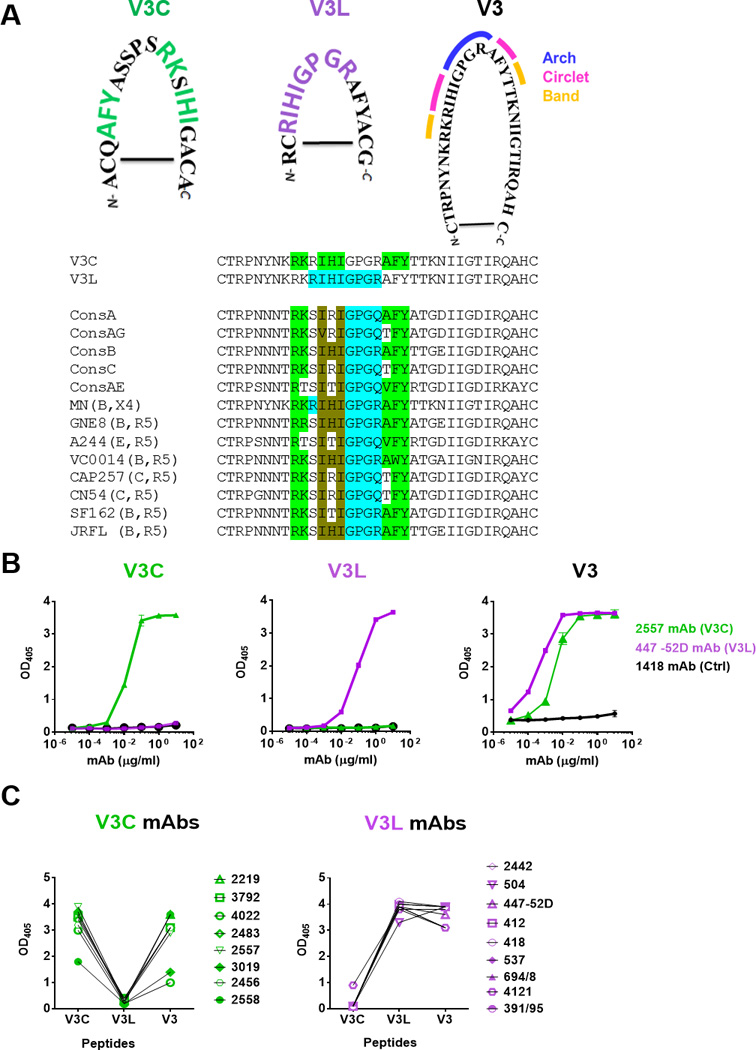
A) Amino acid sequences of cyclic V3C and V3L mimotopes as compared to the full-length cyclic V3 peptide of HIV-1 MN. The signature motifs required for recognition by V3C- and V3L-type mAbs are highlighted in green and purple respectively. The arch, circlet and band regions of the V3 crown [5] are also marked. Alignment of V3 sequences from consensus A, AG, B, C, AE and from the different Env strains used for immunogens in this study shows the presence of the V3C and V3L motifs irrespective of clades and chemokine receptor usage. The specific amino acids encompassing the V3C and V3L motifs are highlighted in green and blue, respectively. The amino acids common for both motifs are shown in brown. The V3L motif is shown to include GPGR or Q at the V3 arch, because V3L-type Abs like 44752D can recognize both sequences [26]. B) Distinct patterns of ELISA reactivity displayed by V3C mAb 2557, V3L mAb 447-52D and control 1418 Abs with the V3C, V3L or full length V3 peptides. Each of these cyclic peptides was biotinylated, coated on the Streptawell ELISA plates (1 µg/ml) and reacted with titrated concentrations of mAbs. C) Specific recognition of V3C and V3L mimotopes by eight V3C- and nine V3L-type mAbs, respectively. Each mAb was tested at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. No cross-reactivity between V3C and V3L mimotopes was observed, whereas the full-length V3 peptide was recognized by both types of the V3 mAbs. OD405, optical density at 405 nm
