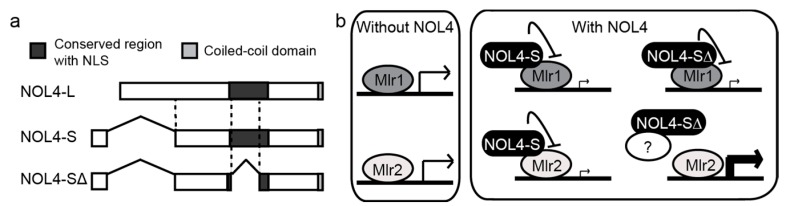
Figure 4.
Mouse NOL4 splicing variants have different functions. (a) Schematics of the splicing variants of mouse NOL4. N-terminal region in NOL4-L is spliced out in NOL4-S and NOL4-SΔ. Major part of the conserved region containing NLS is spliced out in NOL4-SΔ. Adapted with permission from [23]; (b) A model describing how Mlr1 and NOL4 regulate transcription. Left panel: Without NOL4, Mlr1, and Mlr2 show transactivation activities. Right panel: When NOL4 variants are present, NOL4-S directly binds to Mlr1 and Mlr2, and inhibits the transactivation activity. NOL4-SΔ does not directly bind to Mlr2, but it may bind to another cofactor (represented by “?” in the figure), possibly CtBP proteins which suppress the activity of Mlr2, and thereby indirectly increase the transcription activity.