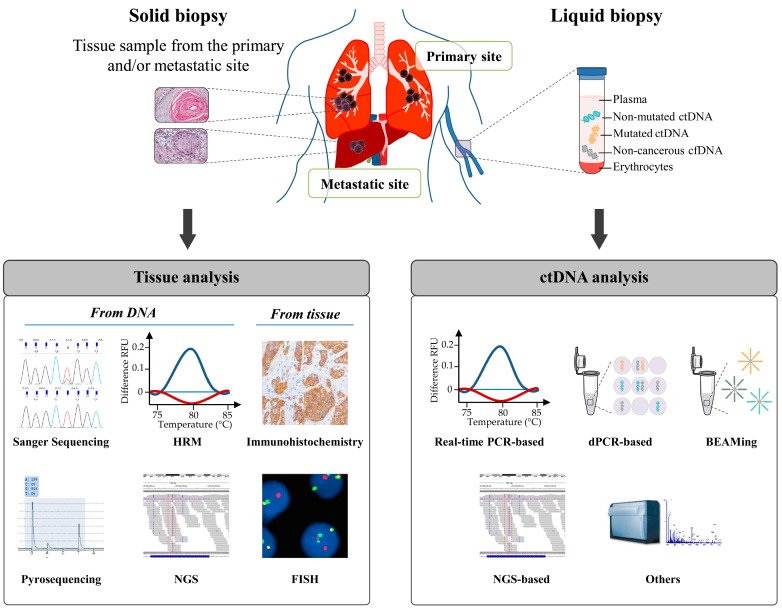
Figure 1.
Overview of the available techniques to detect alterations from solid or liquid biopsies. The left side describes the conventional techniques that use tissue sample as starting material, specifically Sanger sequencing, pyrosequencing, High Resolution Melting (HRM), Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Immunohistochemistry. The right side highlights the different methods available for aberration detections from liquid biopsy. They include, in particular, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based methods, digital PCR (dPCR), Beads, Emulsion, Amplification, and Magnetics (BEAMing) and NGS-based methods. DNA strand in blue corresponds to non-mutated circulating tumoral DNA (ctDNA), in orange to mutated ctDNA and in grey to non-cancerous cell-free DNA (cfDNA). For each technique, a representation of the principle or the result is given as illustration.