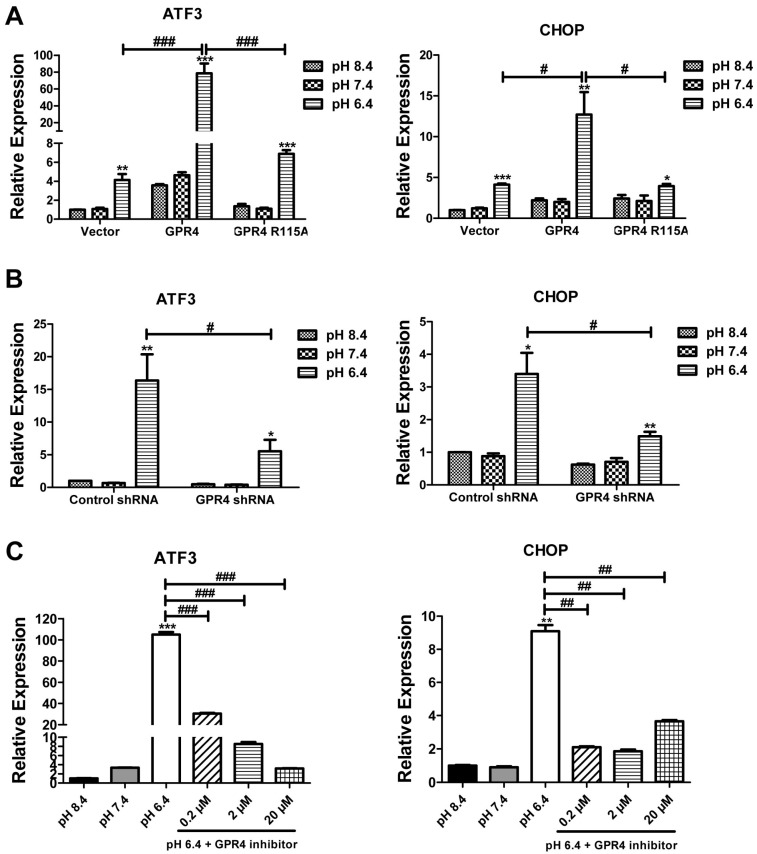
Figure 5.
GPR4 modulates the ER stress response genes induced by acidic pH at the mRNA level in HUVEC. (A,B) HUVEC transduced with the control vector (Vector), GPR4 expression construct (GPR4), GPR4 R115A mutant expression vector (GPR4 R115A), control shRNA (control shRNA), or GPR4 shRNA expression vector (GPR4 shRNA) were treated in EGM-2/HEM buffered media at basic (pH 8.4), physiological (pH 7.4), or acidic (pH 6.4) conditions for 5 h. (C) HUVEC/GPR4 cells were treated for 5 h with EGM-2/HEM pH 8.4, 7.4, or 6.4 media or with pH 6.4 media containing 0.2, 2, and 20 µM of the GPR4 inhibitor, for which one-hour pretreatment in EGM-2 medium with the same concentrations of GPR4 inhibitor was performed. Total RNA was isolated, and cDNA was synthesized. Real-time qRT-PCR was performed to quantify the mRNA level of ATF3 and CHOP. Ct values were normalized to the housekeeping gene β-actin (ACTB). The expression level of the target genes in (A) HUVEC/Vector, (B) HUVEC/control shRNA or (C) HUVEC/GPR4 cells treated with pH 8.4 was set as 1. Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; compared with corresponding pH 8.4 groups. #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001; comparing the indicated pairs of data. The results shown are the average of at least two biological repeats.