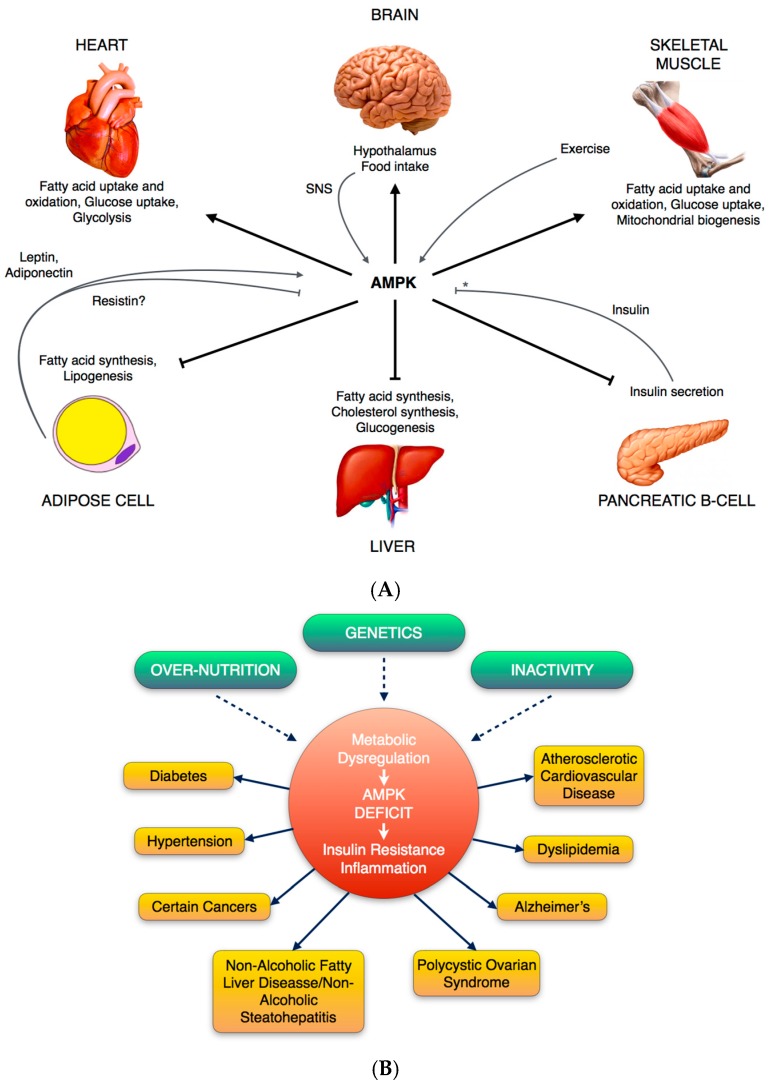
Figure 2.
(A) Diagram of metabolic functions of AMPK in various tissues; Some key metabolic effects are shown. The adipocyte-derived hormones leptin and adiponectin, as well as exercise, activate (grey arrow) AMPK in skeletal muscle, stimulating fatty acid oxidation. Moreover, leptin’s activation of AMPK in skeletal muscle involves the hypothalamic-sympathetic nervous system (SNS) axis. In hypothalamus, AMPK activity plays a role in regulation of food intake. AMPK inhibits (black T-bar) insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells, and insulin inhibits AMPK activation in ischemic heart and hypothalamus, whilst it has no effect on AMPK in skeletal muscle or adipocytes (*). (B) Physiological regulation of AMPK in terms of related diseases and different situations. Overnutrition, inactivity or genetic factors (dashed arrows) can result in a state of dysregulation characterized by inflammation and insulin resistance, that in turn can predispose to one or more of the disorders shown.