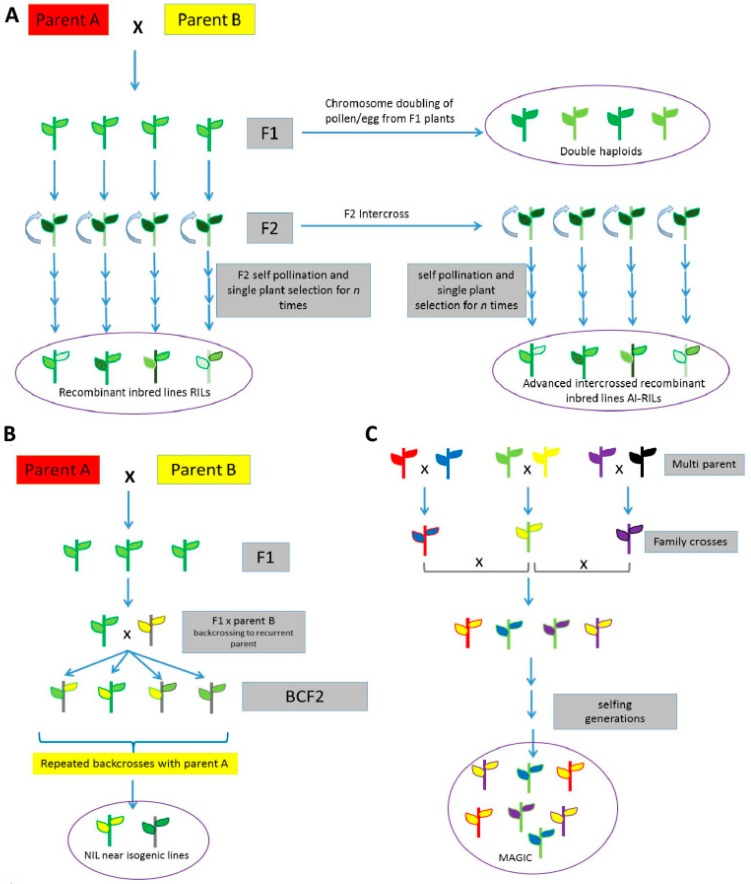
Figure 1.
Population approaches commonly used in genetic studies. Marker-assisted backcrossing or gene pyramiding is the most successful method using genomics information, and are specially used in the introgression (Appendix A) of wild traits. For the identification of genomic regions/genes associated with a certain trait, three major mapping strategies are being used: QTL mapping (linkage mapping), association mapping (linkage disequilibrium mapping) and joint linkage-association mapping (Appendix A). Here are the main population approaches based on initial: bi-parental (A,B); or multi-parental (C) crosses for mapping. (A) F2: Individual F1 plants are self-pollinated to produce an F2 population; Doubled haploids (DH): genotypes formed when haploid cells (pollen/egg) are subjected to chromosome doubling. Recombinant inbred lines (RILs): a population generated from F2 individual plants that are repeatedly self-pollinated n times. Advanced intercrossed recombinant inbred lines (AI-RILs): a population generated by randomly and sequentially intercrossing the F2 lines followed by repeated self-pollinations n times; (B) Backcross inbred lines (BILs): repeated backcrossing (Appendix A) of F1 lines with one of its parents; Near isogenic lines (NILs): backcrossing of F1 with recurrent parent using lines that are identical except for differences in a few genetic loci; and (C) Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC): a population produced by intercrossing families from multiple parents, followed by self-pollination n times.