Figure 5.
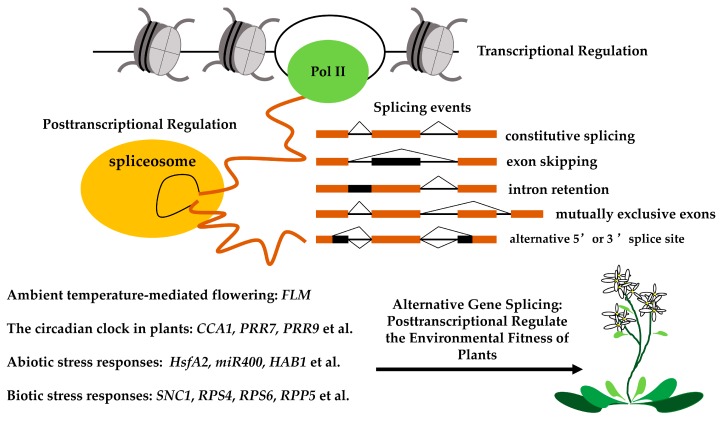
Alternative gene splicing is a novel means of regulating the environmental fitness of plants. Processing of pre-mRNA splicing is initiated during transcription. Splicing is performed by the spliceosome, a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that assembles around splice sites in the introns of a pre-mRNA molecule and then removes the introns catalytically through sequential phosphodiester transfer reactions. One pre-mRNA generate different mRNA isoforms via alternative splicing events, such as usage of an alternative 3′ or 5′ splicing site, exon skipping, intron retention, and mutually exclusive exons. Given their sessile nature, plants must adapt immediately to environmental changes to ensure their survival. Alternative splicing (AS) plays an important role in the environmental fitness of plants through alternative gene splicing.