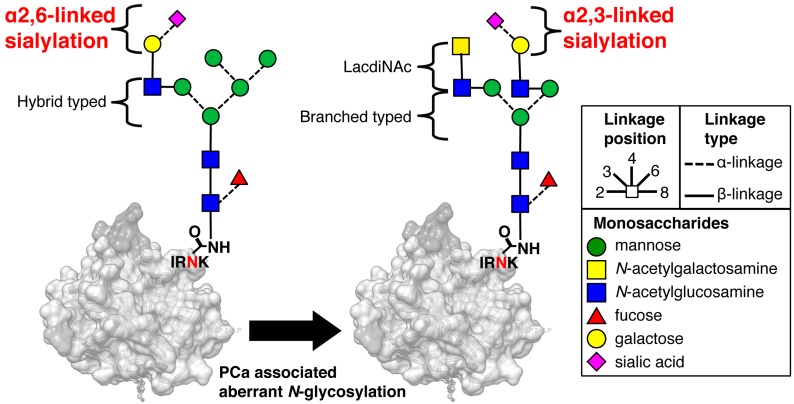
Figure 1.
Prostate cancer-associated aberrant glycosylation of N-glycan on prostate-specific antigen (PSA). In normal PSA, the terminal sialic acids link to galactose residues with an α2,6 linkage whereas in prostate cancer (PCa)-associated PSA, the linkage between the terminal sialic acid and galactose residues is an α2,3 linkage [18]. Carbon linkage positions are denoted by the bond position drawn on each monosaccharide. Ile-Arg-Asn-Lys, (IRNK): N-glycosylation site of PSA.