Figure 3.
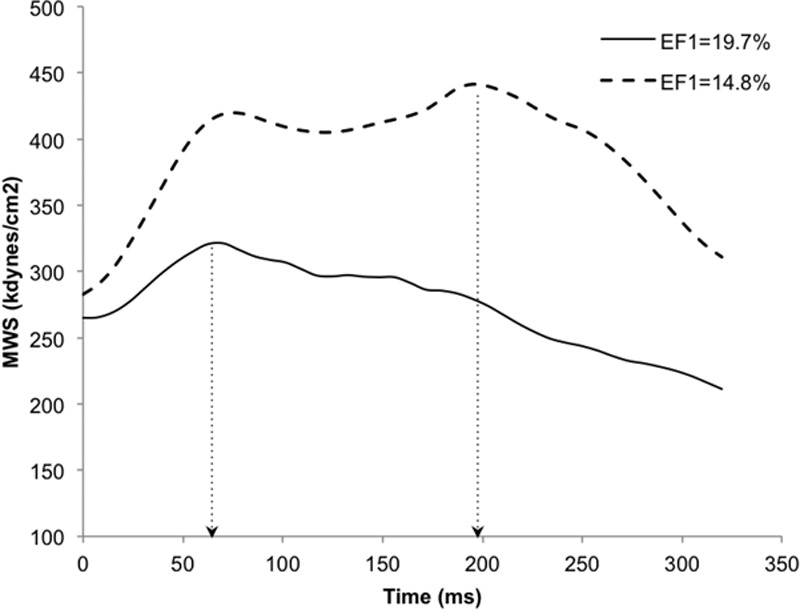
Typical myocardial wall stress traces in a subject with preserved systolic function and first-phase ejection fraction (EF1; solid line, E/E′=8.0, EF1=19.7%) and a subject with impaired diastolic function and reduced EF1 (dashed line, E/E′=16.6, EF1=14.8%) demonstrating longer time to onset of relaxation (TOR, dotted arrows) in the patient with diastolic dysfunction (TOR, 61.2% vs 22.0% of ejection duration). Both subjects had preserved ejection fraction (EF; 63.4% and 63.5%) and similar resting heart rate. E/E′ indicates ratio of mitral valve Doppler early flow (E wave velocity) to tissue Doppler mitral annulus movement (E′ wave velocity; and MWS, myocardial wall stress.
