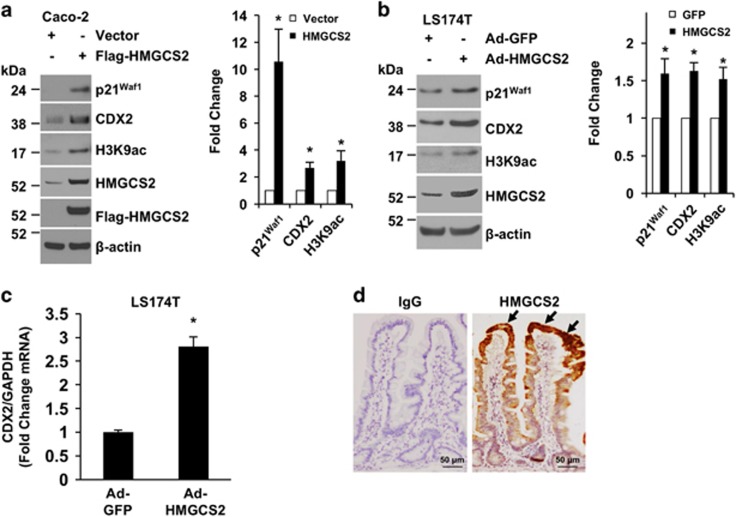
Figure 5.
HMGCS2 contributes to intestinal differentiation. (a) Caco-2 cells were transfected with empty vector (control) or transfected with Flag-HMGCS2 constructs. After 48 h, cells were lysed and extracted for protein. p21Waf1, CDX2, H3K9ac, HMGCS2, Flag-tagged HMGCS2 and β-actin were determined by western blotting. The images are representative of three independent experiments. p21Waf1, CDX2 and H3K9ac signals from three separate experiments were quantitated densitometrically and expressed as fold change with respect to β-actin. (n=3, data represent mean±S.D.; *P<0.01 versus control vector). (b and c) LS174T cells were infected with a recombinant adenovirus encoding the human HMGCS2 or vector control encoding GFP. After 48 h, cells were lysed and extracted for RNA and protein. (b) p21Waf1, CDX2, H3K9ac, HMGCS2 and β-actin were determined by western blotting. The images are representative of three independent experiments. p21Waf1, CDX2 and H3K9ac signals from three separate experiments were quantitated densitometrically and expressed as fold change with respect to β-actin. (n=3, data represent mean±S.D.; *P<0.01 versus GFP control). (c) CDX2 mRNA expression was assessed by real-time RT-PCR. (n=3, data represent mean±S.D.; *P<0.01 versus GFP control). Data are from one of three independent experiments with similar results. Overexpression of HMGCS2 inhibits HDAC and increases p21Waf1 and CDX2 expression in Caco-2 and LS174T cells. (d) Immunohistochemical analysis of HMGCS2 protein expression in normal human small intestine. Human normal small intestine sections were fixed and stained with primary anti-human HMGCS2 antibody. HMGCS2 is specifically expressed in the more differentiated region (i.e., villus; arrows). Scale bars=50 μm. The images are representative of five cases