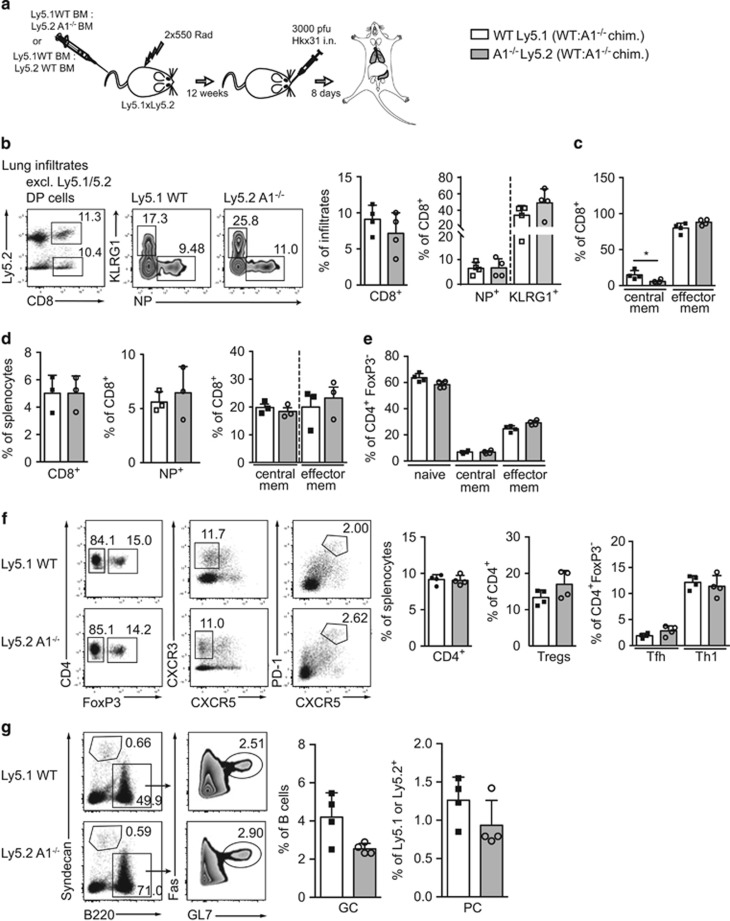
Figure 2.
A1−/− cells in chimaeric mice exhibit normal T cell immune responses in an acute influenza infection model. (a) Schematic overview of the influenza infection workflow: C57BL/6-Ly5.1xLy5.2 F1 mice were lethally irradiated and reconstituted with 1:1 mixed bone-marrow from C57BL/6-Ly5.1 wild-type and C57BL/6-Ly5.2 A1−/− mice. Reconstituted mice were infected intra-nasally (i.n.) with 3000 pfu HKx31 influenza virus and lungs and spleens were analysed 8 days post infection by flow cytometry. (b) Leukocyte infiltrates were isolated from lungs of chimaeric mice by gradient centrifugation. The recovered cells were analysed by flow cytometry for tetramer-positive antigen-specific (NP+) CD8+ T cells, KLRG1+ short-lived CD8+ effector T cells and (c) central (CD44+CD62L+) as well as effector (CD44+CD62L−) memory-like CD8+ T cells. (d) Spleen cells from infected bone-marrow chimaeric mice were isolated and analysed for CD8+ NP+ cells, or central as well as effector memory-like CD8+ T cells. (e) CD4+ splenic T cells were further analysed for CD4+FoxP3− naive (CD62L+CD44-), central or effector memory-like subsets. (f) CD4+ splenic T cells were analysed for FoxP3+ Treg cells, FoxP3−CXCR3+ Th1 cells, and FoxP3−CXCR5+PD-1+ Tfh cells. (g) Spleen cells from infected mice were analysed for Syndecan1+ plasma cells (PC) and B220+FAS+GL7+ germinal centre B cells (GC). Bars represent means±S.E.M. (n=4), irradiation-resistant Ly5.1/5.2 DP cells were excluded by electronic gating